Domain mapping on the human metastasis regulator protein h-Prune reveals a C-terminal dimerization domain
- PMID: 17655525
- PMCID: PMC2049022
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070408
Domain mapping on the human metastasis regulator protein h-Prune reveals a C-terminal dimerization domain
Abstract
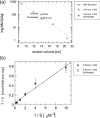
The human orthologue of the Drosophila prune protein (h-Prune) is an interaction partner and regulator of the metastasis suppressor protein NM23-H1 (non-metastatic protein 23). Studies on a cellular breast-cancer model showed that inhibition of the cAMP-specific PDE (phosphodiesterase) activity of h-Prune lowered the incidence of metastasis formation, suggesting that inhibition of h-Prune could be a therapeutic approach towards metastatic tumours. H-Prune shows no sequence similarity with known mammalian PDEs, but instead appears to belong to the DHH (Asp-His-His) superfamily of phosphoesterases. In order to investigate the structure and molecular function of h-Prune, we expressed recombinant h-Prune in a bacterial system. Through sequence analysis and limited proteolysis, we identified domain boundaries and a potential coiled-coil region in a C-terminal cortexillin homology domain. We found that this C-terminal domain mediated h-Prune homodimerization, as well as its interaction with NM23-H1. The PDE catalytic domain of h-Prune was mapped to the N-terminus and shown to be active, even when present in a monomeric form. Our findings indicate that h-Prune is composed of two independent active sites and two interaction sites for the assembly of oligomeric signalling complexes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Nm23-H1-h-Prune complex in cellular physiology: a 'tip of the iceberg' protein network perspective.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Sep;329(1-2):149-59. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0115-4. Epub 2009 Apr 24. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19390954 Review.
-
Understanding h-prune biology in the fight against cancer.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2007;24(8):637-45. doi: 10.1007/s10585-007-9109-3. Epub 2007 Oct 19. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2007. PMID: 17952613 Review.
-
Prune cAMP phosphodiesterase binds nm23-H1 and promotes cancer metastasis.Cancer Cell. 2004 Feb;5(2):137-49. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(04)00021-2. Cancer Cell. 2004. PMID: 14998490
-
Neuroblastoma tumorigenesis is regulated through the Nm23-H1/h-Prune C-terminal interaction.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1351. doi: 10.1038/srep01351. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23448979 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of nm23-H1 by CKI induces its complex formation with h-prune and promotes cell motility.Oncogene. 2008 Mar 20;27(13):1853-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210822. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 17906697
Cited by
-
The Nm23-H1-h-Prune complex in cellular physiology: a 'tip of the iceberg' protein network perspective.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Sep;329(1-2):149-59. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0115-4. Epub 2009 Apr 24. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19390954 Review.
-
Inorganic polyphosphate in platelet rich plasma accelerates re-epithelialization in vitro and in vivo.Regen Ther. 2020 Aug 6;15:138-148. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2020.07.004. eCollection 2020 Dec. Regen Ther. 2020. PMID: 33426212 Free PMC article.
-
The exopolyphosphatase TbrPPX1 of Trypanosoma brucei.BMC Microbiol. 2011 Jan 6;11:4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-4. BMC Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21208463 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding h-prune biology in the fight against cancer.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2007;24(8):637-45. doi: 10.1007/s10585-007-9109-3. Epub 2007 Oct 19. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2007. PMID: 17952613 Review.
-
Functional Genomics of PRUNE1 in Neurodevelopmental Disorders (NDDs) Tied to Medulloblastoma (MB) and Other Tumors.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 22;11:758146. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.758146. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34745995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Florenes V. A., Aamdal S., Myklebost O., Maelandsmo G. M., Bruland O. S., Fodstad O. Levels of nm23 messenger RNA in metastatic malignant melanomas: inverse correlation to disease progression. Cancer Res. 1992;52:6088–6091. - PubMed
-
- Fan Z., Beresford P. J., Oh D. Y., Zhang D., Lieberman J. Tumor suppressor NM23-H1 is a granzyme A-activated DNase during CTL-mediated apoptosis, and the nucleosome assembly protein SET is its inhibitor. Cell. 2003;112:659–672. - PubMed
-
- Steeg P. S. Metastasis suppressors alter the signal transduction of cancer cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2003;3:55–63. - PubMed
-
- Radinsky R., Weisberg H. Z., Staroselsky A. N., Fidler I. J. Expression level of the nm23 gene in clonal populations of metastatic murine and human neoplasms. Cancer Res. 1992;52:5808–5814. - PubMed
-
- Hartsough M. T., Steeg P. S. Nm23/nucleoside diphosphate kinase in human cancers. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2000;32:301–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

