Tea polyphenols for health promotion
- PMID: 17655876
- PMCID: PMC3220617
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.06.011
Tea polyphenols for health promotion
Abstract
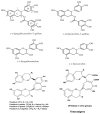
People have been consuming brewed tea from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant for almost 50 centuries. Although health benefits have been attributed to tea, especially green tea consumption since the beginning of its history, scientific investigations of this beverage and its constituents have been underway for less than three decades. Currently, tea, in the form of green or black tea, next to water, is the most widely consumed beverage in the world. In vitro and animal studies provide strong evidence that polyphenols derived from tea may possess the bioactivity to affect the pathogenesis of several chronic diseases. Among all tea polyphenols, epigallocatechin-3-gallate has been shown to be responsible for much of the health promoting ability of green tea. Tea and tea preparations have been shown to inhibit tumorigenesis in a variety of animal models of carcinogenesis. However, with increasing interest in the health promoting properties of tea and a significant rise in scientific investigation, this review covers recent findings on the medicinal properties and health benefits of tea with special reference to cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Adhami VM, Afaq F, Mukhtar H. Insulin-like growth factor-I axis as a pathway for cancer chemoprevention. Clinical Cancer Research. 2006;12(19):5611–5614. - PubMed
-
- Adhami VM, Ahmad N, Mukhtar H. Molecular targets for green tea in prostate cancer prevention. Journal of Nutrition. 2003;133 (7 Suppl):2417S–2424S. - PubMed
-
- Adhami VM, Malik A, Zaman N, Sarfaraz S, Siddiqui IA, Syed DN, Afaq F, Pasha FS, Saleem M, Mukhtar H. Combined inhibitory effects of green tea polyphenols and selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on the growth of human prostate cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Clinical Cancer Research. 2007;13(5):1611–1619. - PubMed
-
- Adhami VM, Siddiqui IA, Ahmad N, Gupta S, Mukhtar H. Oral consumption of green tea polyphenols inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I-induced signalling in an autochthonus mouse model of prostate cancer. Cancer Research. 2004;64 (23):8715–8722. - PubMed
-
- Afaq F, Ahmad N, Mukhtar H. Suppression of UVB-induced phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor kappa B by green tea polyphenol in SKH-1 hairless mice. Oncogene. 2003;22(58):9254–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical