A single acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is required for catabolism of isoleucine, valine and short-chain fatty acids in Aspergillus nidulans
- PMID: 17656140
- PMCID: PMC2905684
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fgb.2007.06.004
A single acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is required for catabolism of isoleucine, valine and short-chain fatty acids in Aspergillus nidulans
Abstract
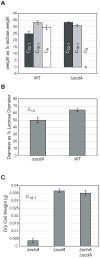
An acyl-CoA dehydrogenase has been identified as part of the mitochondrial beta-oxidation pathway in the ascomycete fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Disruption of the scdA gene prevented use of butyric acid (C(4)) and hexanoic acid (C(6)) as carbon sources and reduced cellular butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase activity by 7.5-fold. While the mutant strain exhibited wild-type levels of growth on erucic acid (C(22:1)) and oleic acid (C(18:1)), some reduction in growth was observed with myristic acid (C(14)). The DeltascdA mutation was found to be epistatic to a mutation downstream in the beta-oxidation pathway (disruption of enoyl-CoA hydratase). The DeltascdA mutant was also unable to use isoleucine or valine as a carbon source. Transcription of scdA was observed in the presence of either fatty acids or amino acids. When the mutant was grown in medium containing either isoleucine or valine, organic acid analysis of culture supernatants showed accumulation of 2-oxo acid intermediates of branched chain amino acid catabolism, suggesting feedback inhibition of the upstream branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase.
Figures




References
-
- Andresen BS, Christensen E, Corydon TJ, Bross P, Pilgaard B, Wanders RJ, Ruiter JP, Simonsen H, Winter V, Knudsen I, Schroeder LD, Gregersen N, Skovby F. Isolated 2-methylbutyrylglycinuria caused by short/branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: identification of a new enzyme defect, resolution of its molecular basis, and evidence for distinct acyl-CoA dehydrogenases in isoleucine and valine metabolism. Am J Hum Genet. 2000;67:1095–1103. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachhawat BK, Coon MJ, Kupiecki FP, Nagle R, Robinson WG. Coenzyme A thiol esters of isobutyric, methacrylic, and beta-hydroxyisobutyric acids as intermediates in the enzymatic degradation of valine. J Biol Chem. 1957;224:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Battaile KP, Mohsen AA, Vockley J. Functional role of the active site glutamate-368 in rat short chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1996;35:15356–15363. - PubMed
-
- Battaile KP, Molin-Case J, Paschke R, Wang M, Bennett D, Vockley J, Kim JJP. Crystal structure of rat short chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase complexed with acetoacetyl-CoA: comparison with other acyl-CoA dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:12200–12207. - PubMed
-
- Brock M, Fischer R, Linder D, Buckel W. Methylcitrate synthase from Aspergillus nidulans: implications for proprionate as an antifungal agent. Mol Microbiol. 2000;35:961–973. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

