High-throughput analysis of signals regulating stem cell fate and function
- PMID: 17656147
- PMCID: PMC2824500
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.05.036
High-throughput analysis of signals regulating stem cell fate and function
Abstract
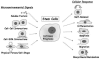
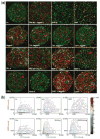
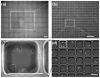
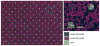
Stem cells exhibit promise in numerous areas of regenerative medicine. Their fate and function are governed by a combination of intrinsic determinants and signals from the local microenvironment, or niche. An understanding of the mechanisms underlying both embryonic and adult stem cell functions has been greatly enhanced by the recent development of several high-throughput technologies: microfabricated platforms, including cellular microarrays, to investigate the combinatorial effects of microenvironmental stimuli and large-scale screens utilizing small molecules and short interfering RNAs to identify crucial genetic and signaling elements. Furthermore, the integration of these systems with other versatile platforms, such as microfluidics and lentiviral microarrays, will continue to enable the detailed elucidation of stem cell processes, and thus, greatly contribute to the development of stem cell based therapies.
Figures

References
-
- Boyer LA, Mathur D, Jaenisch R. Molecular control of pluripotency. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006;16:455–462. - PubMed
-
- Van Hoof D, Passier R, Ward-Van Oostwaard D, Pinkse MW, Heck AJ, Mummery CL, Krijgsveld J. A quest for human and mouse embryonic stem cell-specific proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006;5:1261–1273. - PubMed
-
- Eckfeldt CE, Mendenhall EM, Verfaillie CM. The molecular repertoire of the ‘almighty’ stem cell. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:726–737. - PubMed
-
-
Scadden DT. The stem-cell niche as an entity of action. Nature. 2006;441:1075–1079.. Insightful review of recent advances identifying stem cell niches in multiple organ systems. Important components of stem cell niches are highlighted including paracrine signals, extracellular matrix composition, as well as metabolic elements such as reactive oxygen species and calcium concentrations. The dynamic nature of stem cell microenvironments and the potential for targeting normal or cancer stem cell niches for therapeutic purposes is also discussed.
-
-
- Fuchs E, Tumbar T, Guasch G. Socializing with the neighbors: stem cells and their niche. Cell. 2004;116:769–778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

