Mouse model of erectile dysfunction due to diet-induced diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 17656247
- PMCID: PMC2245873
- DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2007.02.060
Mouse model of erectile dysfunction due to diet-induced diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Objectives: To determine whether diet-induced diabetes mellitus (DM) in mice would reproduce the major features of human erectile dysfunction (ED) because DM is a significant risk factor in the development of ED.
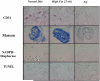
Methods: In total, 150 C57BL6 (bl6) mice were divided into six groups of 25 mice each. Of these 150 mice, 125 were fed a high-fat (45% of total calories) diet for the final 4 (group 2), 8 (group 3), 12 (group 4), 16 (group 5), or 22 (group 6) weeks. Group 1 was fed a normal diet. The mice were 22 to 25 weeks old at study termination. The corporal tissues were harvested and studied for endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent vasoreactivity, endothelial and smooth muscle cell content by immunohistochemistry, nitric oxide synthase expression by nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-diaphorase staining, and apoptosis by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase biotin-D-UTP nick-end labeling staining.
Results: The blood glucose levels were greater in groups 2 to 6 compared with those in group 1. The vasoreactivity, endothelial cell content, and smooth muscle/collagen ratio were lower and apoptosis were greater in the DM mice (P = 0.0001, P = 0.10, P = 0.0002, P <0.001, and P <0.001, respectively). Significantly decreased nitric oxide synthase expression and significantly increased apoptosis (P <0.0001 each) was found in the high-fat diet mice.
Conclusions: Corporal tissue from mice with diet-induced DM demonstrated many of the major functional, structural, and biochemical changes found in humans with ED. This model should serve as a valuable tool for advancing our understanding of the role DM plays in the pathogenesis of ED.
Figures

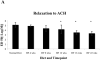
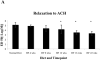
References
-
- Musicki B, Burnett AL. eNOS function and dysfunction in the penis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2006;231:154–165. - PubMed
-
- Lue TF. Erectile dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1802–1813. - PubMed
-
- Siu SC, Lo SK, Wong KW, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in Hong Kong diabetic patients. Diabet Med. 2001;18:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Penson DF, Latini DM, Lubeck DP, et al. Comprehensive Evaluation of Erectile Dysfunction (ExCEED) database.Do impotent men with diabetes have more severe erectile dysfunction and worse quality of life than the general population of impotent patients? Results from the Exploratory Comprehensive Evaluation of Erectile Dysfunction (ExCEED) database. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:1093–1099. - PubMed
-
- Musicki B, Burnett AL. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetic erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2006 Jun 15; [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

