GABAA and glycine receptor-mediated transmission in rat lamina II neurones: relevance to the analgesic actions of neuroactive steroids
- PMID: 17656439
- PMCID: PMC2277187
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.134445
GABAA and glycine receptor-mediated transmission in rat lamina II neurones: relevance to the analgesic actions of neuroactive steroids
Abstract
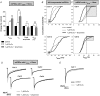
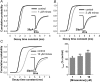
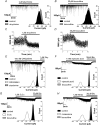
Analgesic neurosteroids such as 5alpha-pregnan-3alpha-ol-20-one (5alpha3alpha) are potent selective endogenous modulators of the GABA(A) receptor (GABA(A)R) while certain synthetic derivatives (i.e. minaxolone) additionally enhance the function of recombinant glycine receptors (GlyR). Inhibitory transmission within the superficial dorsal horn has been implicated in mediating the analgesic actions of neurosteroids. However, the relative contribution played by synaptic and extrasynaptic receptors is unknown. In this study, we have compared the actions of 5alpha3alpha and minaxolone upon inhibitory transmission mediated by both GABA(A) and strychnine-sensitive GlyRs in lamina II neurones of juvenile (P15-21) rats. At the near physiological temperature of 35 degrees C and at a holding potential of -60 mV we recorded three kinetically distinct populations of miniature IPSCs (mIPSCs): GlyR-mediated, GABA(A)R-mediated and mixed GABA(A)R-GlyR mIPSCs, arising from the corelease of both inhibitory neurotransmitters. In addition, sequential application of strychnine and bicuculline revealed a small (5.2 +/- 1.0 pA) GlyR- but not a GABA(A)R-mediated tonic conductance. 5alpha3alpha (1-10 microm) prolonged GABA(A)R and mixed mIPSCs in a concentration-dependent manner but was without effect upon GlyR mIPSCs. In contrast, minaxolone (1-10 microm) prolonged the decay of GlyR mIPSCs and, additionally, was approximately 10-fold more potent than 5alpha3alpha upon GABA(A)R mIPSCs. However, 5alpha3alpha and minaxolone (1 microm) evoked a similar bicuculline-sensitive inhibitory conductance, indicating that the extrasynaptic GABA(A)Rs do not discriminate between these two steroids. Furthermore, approximately 92% of the effect of 1 microm 5alpha3alpha upon GABAergic inhibition could be accounted for by its action upon the extrasynaptic conductance. These findings are relevant to modulation of inhibitory circuits within spinally mediated pain pathways and suggest that extrasynaptic GABA(A)Rs may represent a relevant molecular target for the analgesic actions of neurosteroids.
Figures


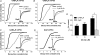

Similar articles
-
Differential contribution of GABAergic and glycinergic components to inhibitory synaptic transmission in lamina II and laminae III-IV of the young rat spinal cord.Eur J Neurosci. 2007 Nov;26(10):2940-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05919.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18001289
-
Transition from GABAergic to glycinergic synaptic transmission in newly formed spinal networks.J Neurophysiol. 2001 Jul;86(1):492-502. doi: 10.1152/jn.2001.86.1.492. J Neurophysiol. 2001. PMID: 11431527
-
Glycine and GABAA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in rat substantia gelatinosa: inhibition by mu-opioid and GABAB agonists.J Physiol. 1998 Mar 1;507 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):473-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.473bt.x. J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9518706 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity and function of extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors during pregnancy and after delivery.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2009 Dec;34 Suppl 1:S74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.06.013. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19608348 Review.
-
Neurosteroid interactions with synaptic and extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors: regulation of subunit plasticity, phasic and tonic inhibition, and neuronal network excitability.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Nov;230(2):151-88. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3276-5. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 24071826 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pre- and postsynaptic inhibitory control in the spinal cord dorsal horn.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013 Mar;1279:90-6. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12056. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013. PMID: 23531006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of glycine receptor single-channel conductance by intracellular phosphorylation.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 16;10(1):4804. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61677-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32179786 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition Mediated by Glycinergic and GABAergic Receptors on Excitatory Neurons in Mouse Superficial Dorsal Horn Is Location-Specific but Modified by Inflammation.J Neurosci. 2017 Mar 1;37(9):2336-2348. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2354-16.2017. Epub 2017 Jan 27. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28130358 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced GABAergic actions resulting from the coapplication of the steroid 3α-hydroxy-5α-pregnane-11,20-dione (alfaxalone) with propofol or diazepam.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 9;8(1):10341. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28754-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29985445 Free PMC article.
-
GABAA and Glycine Receptor-Mediated Inhibitory Synaptic Transmission onto Adult Rat Lamina IIi PKCγ-Interneurons: Pharmacological but Not Anatomical Specialization.Cells. 2022 Apr 15;11(8):1356. doi: 10.3390/cells11081356. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35456035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aitken PG, Breese GR, Dudek FF, Edwards F, Espanol MT, Larkman PM, Lipton P, Newman GC, Nowak TS, Jr, Panizzon KL, Raley-Susman KM, Reid KH, Rice ME, Sarvey JM, Schoepp DD, Segal M, Taylor CP, Teyler TJ, Voulalas PJ. Preparative methods for brain slices: a discussion. J Neurosci Methods. 1995;59:139–149. - PubMed
-
- Baba H, Ji RR, Kohno T, Moore KA, Ataka T, Wakai A, Okamoto M, Woolf CJ. Removal of GABAergic inhibition facilitates polysynaptic A fiber-mediated excitatory transmission to the superficial spinal dorsal horn. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003;24:818–830. - PubMed
-
- Barnard EA, Skolnick P, Olsen RW, Mohler H, Sieghart W, Biggio G, Braestrup C, Bateson AN, Langer SZ. International Union of Pharmacology. XV. Subtypes of γ-aminobutyric acidA receptors: classification on the basis of subunit structure and receptor function. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50:291–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

