The structure of receptor-associated protein (RAP)
- PMID: 17656581
- PMCID: PMC2203372
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.072865407
The structure of receptor-associated protein (RAP)
Abstract
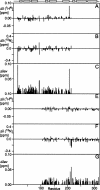
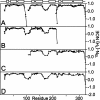
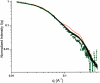
The receptor-associated protein (RAP) is a molecular chaperone that binds tightly to certain newly synthesized LDL receptor family members in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and facilitates their delivery to the Golgi. We have adopted a divide-and-conquer strategy to solve the structures of the individual domains of RAP using NMR spectroscopy. We present here the newly determined structure of domain 2. Based on this structure and the structures of domains 1 and 3, which were solved previously, we utilized experimental small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) data and a novel simulated annealing protocol to characterize the overall structure of RAP. The results reveal that RAP adopts a unique structural architecture consisting of three independent three-helix bundles that are connected by long and flexible linkers. The flexible linkers and the quasi-repetitive structural architecture may allow RAP to adopt various possible conformations when interacting with the LDL receptors, which are also made of repetitive substructure units.
Figures
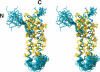

Similar articles
-
Structural organization of the receptor associated protein.Biochemistry. 2003 Dec 23;42(50):14913-20. doi: 10.1021/bi035779e. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 14674767
-
Receptor-associated protein (RAP) has two high-affinity binding sites for the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP): consequences for the chaperone functions of RAP.Biochem J. 2009 Jun 26;421(2):273-82. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090175. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19397492 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of a Potent Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein 1 (LRP1) Antagonist by Engineering a Stable Form of the Receptor-associated Protein (RAP) D3 Domain.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jul 10;290(28):17262-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.660084. Epub 2015 May 26. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26013822 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of receptor-associated protein (RAP) as a molecular chaperone for members of the LDL receptor family.Int Rev Cytol. 2001;209:79-116. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(01)09011-8. Int Rev Cytol. 2001. PMID: 11580203 Review.
-
Combining NMR, SAXS and SANS to characterize the structure and dynamics of protein complexes.Methods Enzymol. 2023;678:263-297. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2022.09.020. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Methods Enzymol. 2023. PMID: 36641211 Review.
Cited by
-
LDL receptor-related protein 1: unique tissue-specific functions revealed by selective gene knockout studies.Physiol Rev. 2008 Jul;88(3):887-918. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00033.2007. Physiol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18626063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant Expression of the Full-length Ectodomain of LDL Receptor-related Protein 1 (LRP1) Unravels pH-dependent Conformational Changes and the Stoichiometry of Binding with Receptor-associated Protein (RAP).J Biol Chem. 2017 Jan 20;292(3):912-924. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.758862. Epub 2016 Dec 12. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 27956551 Free PMC article.
-
PhoX: An IMAC-Enrichable Cross-Linking Reagent.ACS Cent Sci. 2019 Sep 25;5(9):1514-1522. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.9b00416. Epub 2019 Aug 19. ACS Cent Sci. 2019. PMID: 31572778 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing Angiopep-2/LRP1 Molecular Interaction for Optimal Delivery to Glioblastoma (GBM).Molecules. 2022 Oct 8;27(19):6696. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196696. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235232 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolytic regulation of a galectin-3/Lrp1 axis controls osteoclast-mediated bone resorption.J Cell Biol. 2023 Apr 3;222(4):e202206121. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202206121. Epub 2023 Mar 2. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36880731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bax A., Kontaxis, G., and Tjandra, N. 2001. Dipolar couplings in macromolecular structure determination. In Nuclear magnetic resonance of biological macromolecules (eds. T.L. James, V. Dotsch, and U. Schmitz), pp. 127–174. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. Part B. - PubMed
-
- Bewley C.A. and Clore, G.M. 2000. Determination of the relative orientation of the two halves of the domain-swapped dimer of cyanovirin-N in solution using dipolar couplings and rigid body minimization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122: 6009–6016.
-
- Boucher P., Gotthardt, M., Li, W.P., Anderson, R.G.W., and Herz, J. 2003. LRP: Role in vascular wall integrity and protection from atherosclerosis. Science 300: 323–329. - PubMed
-
- Cantor C.R. and Schimmel, P.R. 1980. Biophysical chemistry, Part III: The behavior of biological macromolecules. W.H. Freeman and Company, New York.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

