The responses of HT22 cells to the blockade of mitochondrial complexes and potential protective effect of selenium supplementation
- PMID: 17657281
- PMCID: PMC1925139
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.3.335
The responses of HT22 cells to the blockade of mitochondrial complexes and potential protective effect of selenium supplementation
Abstract
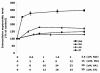
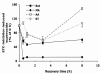
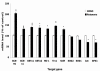
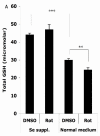
Mitochondria are the major reactive oxygen species (ROS)--generating sites in mammalian cells. Blockade of complexes in the electron transport chain (ETC) increases the leakage of single electrons to O(2) and therefore increases ROS levels. Complexes I and III have been reported to be the major ROS-generating sites in mitochondria. In this study, using mouse hippocampal HT22 cells as in vitro model, we monitored the change of intracellular ROS level in response to the blockade of ETC at different complex, and measured changes of gene expression of antioxidant enzymes and phase II enzymes, also evaluated potential protective effect of selenium (Se) supplementation to the cells under this oxidative stress. In summary, our results showed that complex I was the major ROS-generating site in HT22 cells. Complex I blockade upregulated the mRNA levels of glutamylcysteine synthetase heavy and light chains, glutathione-S-transferases omega1 and alpha 2, hemoxygenase 1, thioredoxin reductase 1, and selenoprotein H. Unexpectedly, the expression of the enzymes that directly scavenge ROS decreased, including superoxide dismutases 1 and 2, glutathione peroxidase 1, and catalase. Se supplementation increased glutathione levels and glutathione peroxidase activity, indicating a potential protective role in oxidative stress caused by ETC blockade.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mitochondria and NADPH oxidases are the major sources of TNF-α/cycloheximide-induced oxidative stress in murine intestinal epithelial MODE-K cells.Cell Signal. 2015 Jun;27(6):1141-58. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.02.019. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Cell Signal. 2015. PMID: 25725292
-
Direct, real-time monitoring of superoxide generation in isolated mitochondria.Free Radic Res. 2009 Sep;43(9):796-802. doi: 10.1080/10715760903062895. Epub 2009 Jun 25. Free Radic Res. 2009. PMID: 19562601
-
Role of mitochondrial electron transport chain complexes in capsaicin mediated oxidative stress leading to apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e20151. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020151. Epub 2011 May 25. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21647434 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide in plant mitochondria: origin and redundant regulatory systems.Physiol Plant. 2010 Apr;138(4):447-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2009.01340.x. Epub 2009 Dec 9. Physiol Plant. 2010. PMID: 20059731 Review.
-
Production of reactive oxygen species in brain mitochondria: contribution by electron transport chain and non-electron transport chain sources.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005 Sep-Oct;7(9-10):1140-9. doi: 10.1089/ars.2005.7.1140. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005. PMID: 16115017 Review.
Cited by
-
Selenite stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis signaling and enhances mitochondrial functional performance in murine hippocampal neuronal cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47910. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047910. Epub 2012 Oct 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23110128 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium preserves mitochondrial function, stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis, and reduces infarct volume after focal cerebral ischemia.BMC Neurosci. 2012 Jul 9;13:79. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-13-79. BMC Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22776356 Free PMC article.
-
Tolfenamic acid inhibits ROS-generating oxidase Nox1-regulated p53 activity in intrastriatal injection of malonic acid rats.J Physiol Sci. 2022 Jul 18;72(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12576-022-00842-4. J Physiol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35850611 Free PMC article.
-
Changes of lysosome by L-serine in rotenone-treated hippocampal neurons.Appl Microsc. 2023 Jan 10;53(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s42649-022-00084-z. Appl Microsc. 2023. PMID: 36626017 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanoparticle Exposure Causes Pulmonary Structural Damage and Mitochondrial Dynamic Imbalance in the Rat: Protective Effects of Sodium Selenite.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Jan 30;15:633-645. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S232986. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32099356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chance B, Sies H, Boveris A. Hydroperoxide metabolism in mammalian organs. Physiol Rev. 1979;59:527–605. - PubMed
-
- Cortopassi C, Wang E Modelling the effects of age-related mtDNA mutationaccumulation:complex I deficiency, superox-ide and cell death. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1995;1271:i7i–i76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

