Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mediates the early increase of blood supply (EIBS) in colon carcinogenesis
- PMID: 17658518
- PMCID: PMC2913280
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.07.012
Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mediates the early increase of blood supply (EIBS) in colon carcinogenesis
Abstract
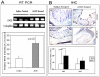
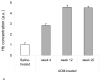
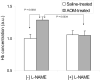
We have recently demonstrated that dramatic alteration in mucosal microvascular blood content termed early increase in blood supply (EIBS) is a hallmark of early colon carcinogenesis. In the current study, we elucidate the mechanism of EIBS by assessing iNOS/nitric oxide axis in the histologically normal colonic mucosa of rats treated with the colon-specific carcinogen, azoxymethane. We demonstrate that there was a strong temporal correlation between EIBS and iNOS expression/activity. Importantly, we also observed that short-term treatment with nitric oxide inhibitor abrogated EIBS. These data indicate that iNOS induction may have a critical role in augmenting the predysplastic mucosal blood supply and thereby fostering colon carcinogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neo-angiogenesis and the premalignant micro-circulatory augmentation of early colon carcinogenesis.Cancer Lett. 2011 Jul 28;306(2):205-13. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.03.008. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Cancer Lett. 2011. PMID: 21493000 Free PMC article.
-
Chemopreventive properties of a selective inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in colon carcinogenesis, administered alone or in combination with celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor.Cancer Res. 2002 Jan 1;62(1):165-70. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11782374
-
Chemoprevention of colonic aberrant crypt foci by an inducible nitric oxide synthase-selective inhibitor.Carcinogenesis. 1999 Apr;20(4):641-4. doi: 10.1093/carcin/20.4.641. Carcinogenesis. 1999. PMID: 10223193
-
COX-2 and iNOS, good targets for chemoprevention of colon cancer.Biofactors. 2000;12(1-4):129-33. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520120120. Biofactors. 2000. PMID: 11216473 Review.
-
Gene mutations and altered gene expression in azoxymethane-induced colon carcinogenesis in rodents.Cancer Sci. 2004 Jun;95(6):475-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2004.tb03235.x. Cancer Sci. 2004. PMID: 15182426 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optical measurement of rectal microvasculature as an adjunct to flexible sigmoidosocopy: gender-specific implications.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2010 Jul;3(7):844-51. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0254. Epub 2010 Jun 22. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2010. PMID: 20570881 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibits growth of human melanoma in vivo and synergizes with chemotherapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 15;16(6):1834-44. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3123. Epub 2010 Mar 9. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20215556 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in biophotonics detection of field carcinogenesis for colon cancer risk stratification.J Cancer. 2013;4(3):251-61. doi: 10.7150/jca.5838. Epub 2013 Mar 15. J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23459690 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Tracing of Spontaneous Regression and Anti-angiogenic Response of Individual Microadenomas during Colon Tumorigenesis.Theranostics. 2015 Apr 1;5(7):724-32. doi: 10.7150/thno.10734. eCollection 2015. Theranostics. 2015. PMID: 25897337 Free PMC article.
-
Neo-angiogenesis and the premalignant micro-circulatory augmentation of early colon carcinogenesis.Cancer Lett. 2011 Jul 28;306(2):205-13. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.03.008. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Cancer Lett. 2011. PMID: 21493000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Vita F, et al. Elevated perioperative serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels in patients with colon carcinoma. Cancer. 2004;100:270–8. - PubMed
-
- Shpitz B, Gochberg S, Neufeld D, Grankin M, Buklan G, Klein E, Bernheim J. Angiogenic switch in earliest stages of human colonic tumorigenesis. Anticancer Res. 2003;23:5153–7. - PubMed
-
- Aotake T, Lu CD, Chiba Y, Muraoka R, Tanigawa N. Changes of angiogenesis and tumor cell apoptosis during colorectal carcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:135–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

