Reliable evaluation of performance level for computer-aided diagnostic scheme
- PMID: 17659245
- PMCID: PMC2039704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2007.04.015
Reliable evaluation of performance level for computer-aided diagnostic scheme
Abstract
Rationale and objectives: Computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) schemes have been developed for assisting radiologists in the detection of various lesions in medical images. The reliable evaluation of CAD schemes is an important task in the field of CAD research.
Materials and methods: Many evaluation approaches have been proposed for evaluating the performance of various CAD schemes in the past. However, some important issues in the evaluation of CAD schemes have not been systematically analyzed. The first important issue is the analysis and comparison of various evaluation methods in terms of certain characteristics. The second includes the analysis of pitfalls in the incorrect use of various evaluation methods and the effective approaches to the reduction of the bias and variance caused by these pitfalls. We attempt to address the first important issue in details in this article by conducting Monte Carlo simulation experiments, and to discuss the second issue in the Discussion section.
Results: No single evaluation method is universally superior to the others; different situations of CAD applications require different evaluation methods, as recommended in this article. Bias and variance in the estimated performance levels caused by various pitfalls can be reduced considerably by the correct use of good evaluation methods.
Conclusions: This article would be useful to researchers in the field of CAD research for selecting appropriate evaluation methods and for improving the reliability of the estimated performance of their CAD schemes.
Figures
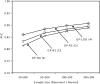
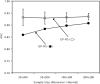
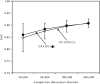
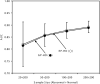
Similar articles
-
Improvement of bias and generalizability for computer-aided diagnostic schemes.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2007 Jun-Jul;31(4-5):338-45. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2007.02.004. Epub 2007 Mar 23. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2007. PMID: 17367995 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of bias and variance for evaluation of computer-aided diagnostic schemes.Med Phys. 2006 Apr;33(4):868-75. doi: 10.1118/1.2179750. Med Phys. 2006. PMID: 16696462
-
Comparison of typical evaluation methods for computer-aided diagnostic schemes: Monte Carlo simulation study.Med Phys. 2007 Mar;34(3):871-6. doi: 10.1118/1.2437130. Med Phys. 2007. PMID: 17441232
-
Anniversary paper: History and status of CAD and quantitative image analysis: the role of Medical Physics and AAPM.Med Phys. 2008 Dec;35(12):5799-820. doi: 10.1118/1.3013555. Med Phys. 2008. PMID: 19175137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computer-aided diagnosis in medical imaging: historical review, current status and future potential.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2007 Jun-Jul;31(4-5):198-211. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2007.02.002. Epub 2007 Mar 8. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2007. PMID: 17349778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Accuracy of a 2-minute eye-tracking assessment to differentiate young children with and without autism.Mol Autism. 2025 Jul 10;16(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s13229-025-00670-4. Mol Autism. 2025. PMID: 40640958 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder Without Expertise: A Pilot Study of 5- to 17-Year-Old Individuals Using Gazefinder.Front Neurol. 2021 Jan 28;11:603085. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.603085. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33584502 Free PMC article.
-
Automated classification of metaphase chromosomes: optimization of an adaptive computerized scheme.J Biomed Inform. 2009 Feb;42(1):22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2008.05.004. Epub 2008 May 21. J Biomed Inform. 2009. PMID: 18585097 Free PMC article.
-
Massive-training support vector regression and Gaussian process for false-positive reduction in computer-aided detection of polyps in CT colonography.Med Phys. 2011 Apr;38(4):1888-902. doi: 10.1118/1.3562898. Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 21626922 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-aided detection; the effect of training databases on detection of subtle breast masses.Acad Radiol. 2010 Nov;17(11):1401-8. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2010.06.009. Epub 2010 Jul 22. Acad Radiol. 2010. PMID: 20650667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan HP, Doi K, Vyborny CJ, Schmidt RA, Metz CE, Lam KL, Ogura T, Wu Y, MacMahon H. Improvement in radiologists' detection of clustered microcalcifications on mammograms: The potential of computer-aided diagnosis. Invest Radiol. 1990;25:1102–1110. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi T, Xu X, MacMahon H, Metz CE, Doi K. Effect of a computer-aided diagnosis scheme on radiologists' performance in detection of lung nodules on radiographs. Radiology. 1996;199:843–848. - PubMed
-
- Fukunaga K, Hayes RR. Effects of sample size on classifier design. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 1989;11:873–885.
-
- Fukunaga K, Hayes RR. Estimation of classifier performance. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 1989;11:1087–1101.
-
- Wagner RF, Chan H-P, Mossoba JT, Sahiner B, Petrick N. Finite-sample effects and resampling plans: applications to linear classifiers in computer-aided diagnosis. Proc SPIE Conf Medical Imaging. 1997;3034:467–477.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

