Compound Danshen injection improves endotoxin-induced microcirculatory disturbance in rat mesentery
- PMID: 17659708
- PMCID: PMC4146797
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i26.3581
Compound Danshen injection improves endotoxin-induced microcirculatory disturbance in rat mesentery
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of compound Danshen injection on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced rat mesenteric microcirculatory dysfunctions and the underlying possible mechanism by an inverted intravital microscope and high-speed video camera system.
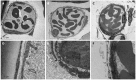
Methods: LPS was continuously infused through the jugular artery of male Wistar rats at the dose of 2 mg/kg per hour. Changes in mesenteric microcirculation, such as diameters of arterioles and venules, velocity of RBCs in venules, leukocyte rolling, adhesion and emigration, free radicals released from post-capillary venules, FITC-albumin leakage and mast cell degranulation, were observed through an inverted intravital microscope assisted with CCD camera and SIT camera. Meanwhile, the expression of adhesion molecules CD11b/CD18 and the production of free radical in neutrophils, and the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were quantified by flow cytometry (FACS) in vitro.
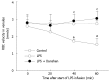
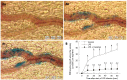
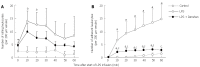
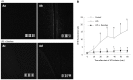
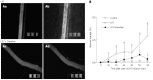
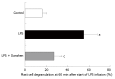
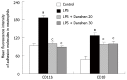
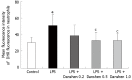
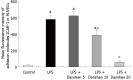
Results: The continuous infusion with LPS resulted in a number of responses in microcirculation, including a significant increase in the positive region of venule stained with Monastral blue B, rolling and adhesion of leukocytes, production of oxygen radical in venular wall, albumin efflux and enhanced mast cell degranulation in vivo, all of which, except for the leukocyte rolling, were attenuated by the treatment with compound Danshen injection. Experiments performed in vitro further revealed that the expression of CD11b/CD18 and the production of oxygen free radical in neutrophils, and the expression of ICAM-1 in HUVECs were increased by exposure to LPS, and they were attenuated by compound Danshen injection.
Conclusion: These results suggest that compound Danshen injection is an efficient drug with multi-targeting potential for improving the microcirculatory disturbance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Total salvianolic acid improves ischemia-reperfusion-induced microcirculatory disturbance in rat mesentery.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Nov 14;16(42):5306-16. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i42.5306. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 21072893 Free PMC article.
-
Improving effect of pretreatment with yiqifumai on LPS-induced microcirculatory disturbance in rat mesentery.Shock. 2009 Sep;32(3):310-6. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31819c36e8. Shock. 2009. PMID: 19174743
-
Potential of 3,4-dihydroxy-phenyl lactic acid for ameliorating ischemia-reperfusion-induced microvascular disturbance in rat mesentery.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Jan;296(1):G36-44. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90284.2008. Epub 2008 Nov 13. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19008340
-
Protective effects of dihydroxylphenyl lactic acid and salvianolic acid B on LPS-induced mesenteric microcirculatory disturbance in rats.Shock. 2008 Feb;29(2):205-11. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318070c61a. Shock. 2008. PMID: 17667359
-
Ameliorating effects of compounds derived from Salvia miltiorrhiza root extract on microcirculatory disturbance and target organ injury by ischemia and reperfusion.Pharmacol Ther. 2008 Feb;117(2):280-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.09.008. Epub 2007 Oct 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18048101 Review.
Cited by
-
A pilot study on investigating the role of Salvia miltiorrhiza in fetal growth restriction.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jun 26;40(6):BSR20201222. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201222. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32406912 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuating effect of pretreatment with Yiqifumai on lipopolysaccharide-induced intestine injury and survival rate in rat.J Inflamm (Lond). 2011 May 2;8:10. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-8-10. J Inflamm (Lond). 2011. PMID: 21535877 Free PMC article.
-
Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen) for Treatment and Prevention of Urolithiasis: A Drosophila Animal Study.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Jan 20;2019:1408979. doi: 10.1155/2019/1408979. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 30800166 Free PMC article.
-
Salvianolic Acid B Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Albumin Leakage from Rat Mesenteric Venules through Src-Regulated Transcelluar Pathway and Paracellular Pathway.PLoS One. 2015 May 19;10(5):e0126640. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126640. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25992563 Free PMC article.
-
Total salvianolic acid improves ischemia-reperfusion-induced microcirculatory disturbance in rat mesentery.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Nov 14;16(42):5306-16. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i42.5306. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 21072893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darcissac EC, Bahr GM, Parant MA, Chedid LA, Riveau GJ. Selective induction of CD11a,b,c/CD18 and CD54 expression at the cell surface of human leukocytes by muramyl peptides. Cell Immunol. 1996;169:294–301. - PubMed
-
- Harris NR, Russell JM, Granger DN. Mediators of endotoxin-induced leukocyte adhesion in mesenteric postcapillary venules. Circ Shock. 1994;43:155–160. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda T, Funaba M. Altered function of murine mast cells in response to lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan. Immunol Lett. 2003;88:21–26. - PubMed
-
- Kurose I, Suematsu M, Miura S, Fukumura D, Sekizuka E, Nagata H, Oshio C, Tsuchiya M. Oxyradical generation from leukocytes during endotoxin-induced microcirculatory disturbance in rat mesentery--attenuating effect of cetraxate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1993;120:37–44. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki H, Suematsu M, Miura S, Liu YY, Watanabe K, Miyasaka M, Tsurufuji S, Tsuchiya M. Rat CINC/gro: a novel mediator for locomotive and secretagogue activation of neutrophils in vivo. J Leukoc Biol. 1994;55:652–657. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

