Sm-like protein Hfq: location of the ATP-binding site and the effect of ATP on Hfq-- RNA complexes
- PMID: 17660259
- PMCID: PMC2206964
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.072883707
Sm-like protein Hfq: location of the ATP-binding site and the effect of ATP on Hfq-- RNA complexes
Abstract
Sm-like proteins are ubiquitous ring-shaped oligomers that exhibit a variety of nucleic acid-binding activities. They have been linked functionally to various cellular events involving RNA, and it is generally believed that their activity is exerted via the passive binding of nucleic acids. Our earlier studies of the Sm-like Escherichia coli protein Hfq provided the first evidence indicating that Hfq is an ATP-binding protein. Using a combination of biochemical and genetic techniques, we have now determined a plausible ATP-binding site in Hfq and tested Hfq's ATP-binding affinity and stoichiometry. The results of RNA footprinting and binding analyses suggest that ATP binding by the Hfq-RNA complex results in its significant destabilization. RNA footprinting indicates deprotection of Hfq-bound RNA tracts in the presence of ATP, suggestive of their release by the protein. The results reported herein broaden the scope of potential in vivo roles for Hfq and other Sm-like proteins.
Figures
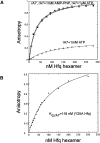
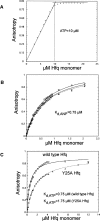
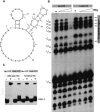


References
-
- Arluison V., Derreumaux, P., Allemand, F., Folichon, M., Hajnsdorf, E., and Régnier, P. 2002. Structural modeling of the Sm-like protein Hfq from Escherichia coli . J. Mol. Biol. 320 705–712. - PubMed
-
- Arluison V., Mura, C., Guzman, M.R., Liquier, J., Pellegrini, O., Gingery, M., Regnier, P., and Marco, S. 2006. Three-dimensional structures of fibrillar Sm proteins: Hfq and other Sm-like proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 356 86–96. - PubMed
-
- Azam T.A., Hiraga, S., and Ishihama, A. 2000. Two types of localization of the DNA-binding proteins within the Escherichia coli nucleoid. Genes Cells 5 613–626. - PubMed
-
- DuBow M.S., Ryan, T., Young, R.A., and Blumenthal, T. 1977. Host factor for coliphage Q β RNA replication: Presence in procaryotes and association with the 30S ribosomal subunit in Escherichia coli . Mol. Gen. Genet. 153 39–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

