Modeling fatty acid delivery from intestinal fatty acid binding protein to a membrane
- PMID: 17660261
- PMCID: PMC2206986
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.072875307
Modeling fatty acid delivery from intestinal fatty acid binding protein to a membrane
Abstract
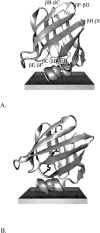
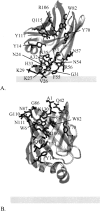
Intestinal fatty acid binding protein (IFABP) interacts with biological membranes and delivers fatty acid (FA) into them via a collisional mechanism. However, the membrane-bound structure of the protein and the pathway of FA transfer are not precisely known. We used molecular dynamics (MD) simulations with an implicit membrane model to determine the optimal orientation of apo- and holo-IFABP (bound with palmitate) on an anionic membrane. In this orientation, the helical portal region, delimited by the alphaII helix and the betaC-betaD and betaE-betaF turns, is oriented toward the membrane whereas the putative beta-strand portal, delimited by the betaB-betaC, betaF-betaG, betaH-betaI turns and the N terminus, is exposed to solvent. Starting from the MD structure of holo-IFABP in the optimal orientation relative to the membrane, we examined the release of palmitate via both pathways. Although the domains can widen enough to allow the passage of palmitate, fatty acid release through the helical portal region incurs smaller conformational changes and a lower energetic cost.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Protein-membrane interaction and fatty acid transfer from intestinal fatty acid-binding protein to membranes. Support for a multistep process.J Biol Chem. 2006 May 19;281(20):13979-89. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511943200. Epub 2006 Mar 21. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16551626
-
Characterization of fatty acid binding and transfer from Δ98Δ, a functional all-β abridged form of IFABP.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Dec;1841(12):1733-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.09.022. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 25311169
-
The integrity of the alpha-helical domain of intestinal fatty acid binding protein is essential for the collision-mediated transfer of fatty acids to phospholipid membranes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Apr;1781(4):192-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.01.005. Epub 2008 Feb 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18284926 Free PMC article.
-
Enterocyte fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs): different functions of liver and intestinal FABPs in the intestine.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2015 Feb;93:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2014.10.001. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2015. PMID: 25458898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thermodynamics of fatty acid transfer.J Membr Biol. 2000 Jul 15;176(2):101-9. doi: 10.1007/s00232001080. J Membr Biol. 2000. PMID: 10926675 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of negative membrane curvature generation by I-BAR domains.Structure. 2021 Dec 2;29(12):1440-1452.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2021.07.010. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Structure. 2021. PMID: 34520736 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamics study of the interaction between fatty acid binding proteins with palmitate mini-micelles.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Jun;326(1-2):29-33. doi: 10.1007/s11010-008-0010-4. Epub 2009 Jan 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19118410
-
Interaction of enterocyte FABPs with phospholipid membranes: clues for specific physiological roles.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Jul-Aug;1811(7-8):452-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.04.005. Epub 2011 Apr 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21539932 Free PMC article.
-
Millisecond timescale dynamics of human liver fatty acid binding protein: testing of its relevance to the ligand entry process.Biophys J. 2010 Jun 16;98(12):3054-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.03.047. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20550918 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the interaction of brain fatty acid binding protein (B-FABP) with model membranes.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60198. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060198. Epub 2013 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakowies D. and van Gunsteren, W.F. 2002. Simulations of apo and holo-fatty acid binding protein: Structure and dynamics of protein, ligand and internal water. J. Mol. Biol. 315 713–736. - PubMed
-
- Balendiran G.K., Schnütgen, F., Scapin, G., Börchers, T., Xhong, N., Lim, K., Godbout, R., Spener, F., and Sacchettini, J.C. 2000. Crystal structure and thermodynamic analysis of human brain fatty acid-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 275 27045–27054. - PubMed
-
- Brooks B.R., Bruccoleri, R.E., Olafson, B.D., States, D.J., Swaminathan, S., and Karplus, M. 1983. Charmm—A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 4 187–217.
-
- Cistola D.P., Kim, K., Rogl, H., and Frieden, C. 1996. Fatty acid interactions with a helix-less variant of intestinal fatty acid-binding protein. Biochemistry 35 7559–7565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

