M protein from Streptococcus pyogenes induces tissue factor expression and pro-coagulant activity in human monocytes
- PMID: 17660410
- PMCID: PMC2885617
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.2006/003285-0
M protein from Streptococcus pyogenes induces tissue factor expression and pro-coagulant activity in human monocytes
Abstract
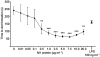
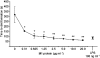
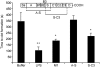
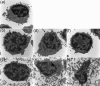
Invasive infections caused by the important pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes are often associated with disturbed blood coagulation in the human host, and may in severe cases develop into the life-threatening condition disseminated intravascular coagulation. In this study, the addition of M1 protein to human blood or purified peripheral blood mononuclear cells led to a dose-dependent increase of pro-coagulant activity, which was mediated by an upregulation of tissue factor on monocytes. Analysis of the resulting clots by transmission electron microscopy revealed that the cells were covered with a fibrin network that seemed to originate from the cell surface. Taken together, the results imply an important role for M proteins in the induction of haemostatic disorders in invasive streptococcal infectious diseases.
Figures
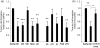
Similar articles
-
A novel role for pro-coagulant microvesicles in the early host defense against streptococcus pyogenes.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(8):e1003529. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003529. Epub 2013 Aug 1. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23935504 Free PMC article.
-
The nonideal coiled coil of M protein and its multifarious functions in pathogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;715:197-211. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-0940-9_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21557065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between surface proteins of Streptococcus pyogenes and coagulation factors modulate clotting of human plasma.J Thromb Haemost. 2003 Feb;1(2):284-91. doi: 10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00105.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2003. PMID: 12871502
-
Streptococcal M protein: a multipotent and powerful inducer of inflammation.J Immunol. 2006 Jul 15;177(2):1221-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.2.1221. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16818781
-
Host-pathogen interactions in Streptococcus pyogenes infections, with special reference to puerperal fever and a comment on vaccine development.Vaccine. 2004 Dec 6;22 Suppl 1:S9-S14. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.08.010. Vaccine. 2004. PMID: 15576204 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel role for pro-coagulant microvesicles in the early host defense against streptococcus pyogenes.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(8):e1003529. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003529. Epub 2013 Aug 1. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23935504 Free PMC article.
-
The nonideal coiled coil of M protein and its multifarious functions in pathogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;715:197-211. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-0940-9_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21557065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streptococcal M1 protein-provoked CXC chemokine formation, neutrophil recruitment and lung damage are regulated by Rho-kinase signaling.J Innate Immun. 2012;4(4):399-408. doi: 10.1159/000336182. Epub 2012 Mar 16. J Innate Immun. 2012. PMID: 22433673 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of group A streptococcal virulence determinants to the pathogenesis of sepsis.Virulence. 2014 Jan 1;5(1):127-36. doi: 10.4161/viru.26400. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Virulence. 2014. PMID: 24157731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vigilant keratinocytes trigger pathogen-associated molecular pattern signaling in response to streptococcal M1 protein.Infect Immun. 2015 Dec;83(12):4673-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00887-15. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26416902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham, E., Reinhart, K., Opal, S., Demeyer, I., Doig, C., Rodriguez, A. L, Beale, R., Svoboda, P., Laterre, P. F. & other authors (2003). Efficacy and safety of tifacogin (recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor) in severe sepsis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 290, 238–247. - PubMed
-
- Berge, A. & Björck, L. (1995). Streptococcal cysteine proteinase releases biologically active fragments of streptococcal surface proteins. J Biol Chem 270, 9862–9867. - PubMed
-
- Bisno, A. L., Brito, M. O. & Collins, C. M. (2003). Molecular basis of group A streptococcal virulence. Lancet Infect Dis 3, 191–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

