Cdc15 is required for spore morphogenesis independently of Cdc14 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 17660551
- PMCID: PMC2013696
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.076133
Cdc15 is required for spore morphogenesis independently of Cdc14 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
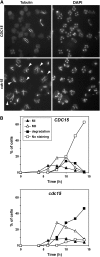
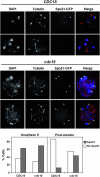
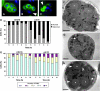
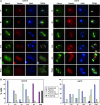
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae exit from mitosis requires the Cdc14 phosphatase to reverse CDK-mediated phosphorylation. Cdc14 is released from the nucleolus by the Cdc14 early anaphase release (FEAR) and mitotic exit network (MEN) pathways. In meiosis, the FEAR pathway is essential for exit from anaphase I. The MEN component Cdc15 is required for the formation of mature spores. To analyze the role of Cdc15 during sporulation, a conditional mutant in which CDC15 expression was controlled by the CLB2 promoter was used. Cdc15-depleted cells proceeded normally through the meiotic divisions but were unable to properly disassemble meiosis II spindles. The morphology of the prospore membrane was aberrant and failed to capture the nuclear lobes. Cdc15 was not required for Cdc14 release from the nucleoli, but it was essential to maintain Cdc14 released and for its nucleo-cytoplasmic transport. However, cells carrying a CDC14 allele with defects in nuclear export (Cdc14-DeltaNES) were able to disassemble the spindle and to complete spore formation, suggesting that the Cdc14 nuclear export defect was not the cause of the phenotypes observed in cdc15 mutants.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cdc14 activates cdc15 to promote mitotic exit in budding yeast.Curr Biol. 2000 May 18;10(10):615-8. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00491-7. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 10837230
-
A Noncanonical Hippo Pathway Regulates Spindle Disassembly and Cytokinesis During Meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2020 Oct;216(2):447-462. doi: 10.1534/genetics.120.303584. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Genetics. 2020. PMID: 32788308 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc14 Early Anaphase Release, FEAR, Is Limited to the Nucleus and Dispensable for Efficient Mitotic Exit.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 19;10(6):e0128604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128604. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26090959 Free PMC article.
-
At the interface between signaling and executing anaphase--Cdc14 and the FEAR network.Genes Dev. 2004 Nov 1;18(21):2581-95. doi: 10.1101/gad.1247304. Genes Dev. 2004. PMID: 15520278 Review.
-
Mitotic exit: the Cdc14 double cross.Curr Biol. 2002 Jul 23;12(14):R482-84. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00963-6. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12176346 Review.
Cited by
-
The Mitotic Exit Network Regulates Spindle Pole Body Selection During Sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2017 Jun;206(2):919-937. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.194522. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28450458 Free PMC article.
-
The anaphase promoting complex targeting subunit Ama1 links meiotic exit to cytokinesis during sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jan;20(1):134-45. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-06-0615. Epub 2008 Oct 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 18946082 Free PMC article.
-
A knockout screen for protein kinases required for the proper meiotic segregation of chromosomes in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Cell Cycle. 2013 Feb 15;12(4):618-24. doi: 10.4161/cc.23513. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23370392 Free PMC article.
-
The Cdc14 Phosphatase Controls Resolution of Recombination Intermediates and Crossover Formation during Meiosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 10;22(18):9811. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189811. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575966 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane and organelle rearrangement during ascospore formation in budding yeast.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024 Sep 26;88(3):e0001324. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00013-24. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38899894 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bardin, A. J., and A. Amon, 2001. MEN and SIN: What's the difference? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2: 815–826. - PubMed
-
- Bembenek, J., J. Kang, C. Kurischko, B. Li, J. R. Raab et al., 2005. Crm1-mediated nuclear export of Cdc14 is required for the completion of cytokinesis in budding yeast. Cell Cycle 4: 961–971. - PubMed
-
- Buonomo, S. B., K. P. Rabitsch, J. Fuchs, S. Gruber, M. Sullivan et al., 2003. Division of the nucleolus and its release of CDC14 during anaphase of meiosis I depends on separase, SPO12, and SLK19. Dev. Cell. 4: 727–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

