Containment versus impingement: finding a compromise for cup placement in total hip arthroplasty
- PMID: 17661036
- PMCID: PMC2267522
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-007-0429-3
Containment versus impingement: finding a compromise for cup placement in total hip arthroplasty
Abstract
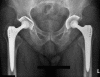
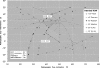
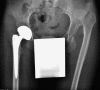
Recommendations for cup containment and impingement may provide conflicting directions for component orientation in total hip arthroplasty. For optimal containment, the cup is positioned with respect to the acetabular bone, resulting in coincidence of the rim of the cup and the acetabulum. This results in good coverage and symmetric load transfer, leading to good long-term stability, but occasionally necessitates more abduction of the cup than that recommended by the safe zone. On the other hand, placement of the cup for an optimal range of motion would lead to only partial containment, with a higher risk of component loosening and revision. The most effective compromise is to use a prosthesis that has a large safe zone, realised by a high head-to-neck ratio, and orienting the cup such that a good containment is achieved and the safe zone is respected. Computer navigation or smart aiming devices may help to find the best relative orientation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The impact of the CCD-angle on range of motion and cup positioning in total hip arthroplasty.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2005 Aug;20(7):723-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2005.04.003. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2005. PMID: 15964112
-
The safe-zones for combined cup and neck anteversions that fulfill the essential range of motion and their optimum combination in total hip replacements.J Biomech. 2006;39(7):1315-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2005.03.008. J Biomech. 2006. PMID: 15894324
-
Understanding acetabular cup orientation: the importance of convention and defining the safe zone.Hip Int. 2011 Nov-Dec;21(6):646-52. doi: 10.5301/HIP.2011.8858. Hip Int. 2011. PMID: 22135016
-
[Whether bone quality matters or not in durability of total hip arthroplasty? Bone quality matters in durability of total hip arthroplasty].Clin Calcium. 2011 May;21(5):746-50. Clin Calcium. 2011. PMID: 21532126 Review. Japanese.
-
Computer navigation in total hip replacement: a meta-analysis.Int Orthop. 2009 Jun;33(3):593-7. doi: 10.1007/s00264-008-0539-6. Epub 2008 Apr 3. Int Orthop. 2009. PMID: 18386003 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pelvic tilt is minimally changed by total hip arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013 Feb;471(2):417-21. doi: 10.1007/s11999-012-2581-3. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013. PMID: 23001502 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of femoral neck osteotomy on femoral component position of a primary cementless total hip arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2015 Dec;39(12):2315-21. doi: 10.1007/s00264-015-2739-1. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Int Orthop. 2015. PMID: 25787684
-
Improving cup positioning using a mechanical navigation instrument.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011 Feb;469(2):423-8. doi: 10.1007/s11999-010-1553-8. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011. PMID: 20852974 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of center of rotation and balance of THR.J Orthop. 2018 Sep 6;15(4):992-996. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2018.08.040. eCollection 2018 Dec. J Orthop. 2018. PMID: 30224857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validation of the femoral anteversion measurement method used in imageless navigation.Comput Aided Surg. 2012;17(4):187-97. doi: 10.3109/10929088.2012.690230. Epub 2012 Jun 8. Comput Aided Surg. 2012. PMID: 22681336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1549338', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1549338/'}]}
- Elke R, Marugg S (1992) Transmission of force to the trabecular structures of the proximal end of the femur (in German). Orthopäde 21:51–56 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9547812', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9547812/'}]}
- Laursen JO, Petersen B, Mossing NB (1998) The Richards Series 2 total hip prosthesis: a 13-year study and radiographic evaluation. Orthopedics 21:277–282 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '641088', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/641088/'}]}
- Lewinnek GE, Lewis JL, Tarr R, Compere CL, Zimmermann JR (1978) Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am 60(2):217–220 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1729002', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1729002/'}]}
- Morscher EW (1992) Current status of acetabular fixation in primary total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 274:172–193 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0883-5403(00)91337-8', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0883-5403(00)91337-8'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10654469', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10654469/'}]}
- Massin P, Geais L, Astoin E, Simondi M, Lavaste F (2000) The anatomic basis for the concept of lateralized femoral stems: a frontal plane radiographic study of the proximal femur. J Arthroplasty 15:93–101 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

