A large Legionnaires' disease outbreak in Pamplona, Spain: early detection, rapid control and no case fatality
- PMID: 17662166
- PMCID: PMC2870864
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268807009077
A large Legionnaires' disease outbreak in Pamplona, Spain: early detection, rapid control and no case fatality
Abstract
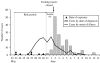
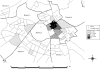
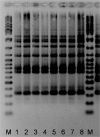
An outbreak of Legionnaire's disease was detected in Pamplona, Spain, on 1 June 2006. Patients with pneumonia were tested to detect Legionella pneumophila antigen in urine (Binax Now; Binax Inc., Scarborough, ME, USA), and all 146 confirmed cases were interviewed. The outbreak was related to district 2 (22 012 inhabitants), where 45% of the cases lived and 50% had visited; 5% lived in neighbouring districts. The highest incidence was found in the resident population of district 2 (3/1000 inhabitants), section 2 (14/1000). All 31 cooling towers of district 2 were analysed. L. pneumophila antigen (Binax Now) was detected in four towers, which were closed on 2 June. Only the strain isolated in a tower situated in section 2 of district 2 matched all five clinical isolates, as assessed by mAb and two genotyping methods, AFLP and PFGE. Eight days after closing the towers, new cases ceased appearing. Early detection and rapid coordinated medical and environmental actions permitted immediate control of the outbreak and probably contributed to the null case fatality.
Figures
References
-
- Dondero TJ et al. An outbreak of Legionnaires' disease associated with a contaminated air-conditioning cooling tower. New England Journal of Medicine. 1980;302:365–370. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Legionnaires' disease associated with cooling towers. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 1994;43:491–499. - PubMed
-
- Brown CM et al. A community outbreak of Legionnaires' disease linked to hospital cooling towers: an epidemiological method to calculate dose of exposure. International Journal of Epidemiology. 1999;28:353–359. - PubMed
-
- Sabria M et al. A community outbreak of Legionnaires' disease: evidence of a cooling tower as the source. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 2006;12:642–647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

