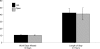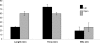Laparoscopic appendectomy in patients with a body mass index of 25 or greater: results of a double blind, prospective, randomized trial
- PMID: 17663093
- PMCID: PMC3015793
Laparoscopic appendectomy in patients with a body mass index of 25 or greater: results of a double blind, prospective, randomized trial
Abstract
Background: The reported advantages of the laparoscopic approach to appendectomy are shortened hospital stay, less postoperative pain, and earlier return to usual activities (work). However, a prospective, randomized, double-blind trial comparing laparoscopic appendectomy with open appendectomy in active-duty males failed to disclose a benefit of laparoscopic appendectomy with regards to postoperative pain and return to work. The aim of our study was to compare open and laparoscopic appendectomy in overweight patients.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, randomized, double-blind study to determine whether laparoscopic appendectomy or the open procedure in overweight patients offers a significant reduction in lost workdays, postoperative pain, or operative time from. Open appendectomy in overweight patients (those with a body mass index > or =25) may be more difficult due to excessive subcutaneous adipose tissue. The open incision may be of considerable size, which may result in increased postoperative pain and a prolonged convalescence.
Results: There was a statistically significant increase in operative time for laparoscopic appendectomy of 11 minutes. As expected, the aggregate incision length for open appendectomy was twice that of the laparoscopic appendectomy.
Conclusion: The data from this prospective, randomized, double-blind study failed to demonstrate any significant reduction in lost workdays, postoperative pain, or operative time with laparoscopic appendectomy.
Figures
References
-
- Mutter D, Vix M, Bui A, et al. Laparoscopy not recommended for routine appendectomy in men: results of a prospective randomized study. Surgery. 1996;120:71–74 - PubMed
-
- McCahill L, Pellegrini C, Wiggins T, Helton W. A clinical outcome and cost analysis of laparoscopic versus open appendectomy. Am J Surg. 1996;171:533–537 - PubMed
-
- Enochsson L, Hellberg A, Rudberg C, et al. Laparoscopic vs open appendectomy in overweight patients. Surg Endosc. 2001;15:387–392 - PubMed
-
- Ignacio R, Burke R, Spencer D, Bissell C, Dorsainvil C, Lucha P. Laparoscopic versus open appendectomy - what is the real difference? Results of a prospective randomized double blinded trial. Surg Endosc. 2004;18:334–337 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials