Six Minute Walk Test to assess functional capacity in chronic liver disease patients
- PMID: 17663517
- PMCID: PMC4171175
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3996
Six Minute Walk Test to assess functional capacity in chronic liver disease patients
Abstract
Aim: To examine the utility of Six Minute Walk Test (6MWT) in patients with chronic liver disease (CLD).
Methods: Two hundred and fifty subjects between the ages of 18 and 80 (mean 47) years performed 6MWT and the Six Minute Walk Distance (6MWD) was measured.
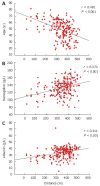
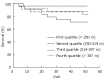
Results: The subjects were categorized into four groups. Group A (n = 45) healthy subjects (control); group B (n = 49) chronic hepatitis B patients; group C (n = 54) chronic hepatitis C patients; group D (n = 98) liver cirrhosis patients. The four groups differed in terms of 6MWDs (P < 0.001). The longest distance walked was 421 +/- 47 m by group A, then group B (390 +/- 53 m), group C (357 +/- 72 m) and group D (306 +/- 111 m). The 6MWD correlated with age (r = -0.482, P < 0.01), hemoglobin (r = 0.373, P < 0.001) and albumin (r = 0.311, P < 0.001) levels. The Child-Pugh classification was negatively correlated with the 6MWD in cirrhosis (group D) patients (r = -0.328, P < 0.01). At the end of a 12 mo follow-up period, 15 of the 98 cirrhosis patients had died from disease complications. The 6MWD for the surviving cirrhotic patients was longer than for non-survivors (317 +/- 101 vs 245 +/- 145 m, P = 0.021; 95% CI 11-132). The 6MWD was found to be an independent predictor of survival (P = 0.024).
Conclusion: 6MWT is a useful tool for assessing physical function in CLD patients. We suggest that 6MWD may serve as a prognostic indicator in patients with liver cirrhosis.
Figures
References
-
- Foster GR, Goldin RD, Thomas HC. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection causes a significant reduction in quality of life in the absence of cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1998;27:209–212. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi G, Loguercio C, Sgarbi D, Abbiati R, Chen CH, Di Pierro M, Disalvo D, Natale S, Marchesini G. Reduced quality of life in patients with chronic hepatitis C: effects of interferon treatment. Dig Liver Dis. 2000;32:398–405. - PubMed
-
- Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Amodio P, Salerno F, Merli M, Panella C, Loguercio C, Apolone G, Niero M, Abbiati R. Factors associated with poor health-related quality of life of patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:170–178. - PubMed
-
- Sainz-Barriga M, Baccarani U, Scudeller L, Risaliti A, Toniutto PL, Costa MG, Ballestrieri M, Adani GL, Lorenzin D, Bresadola V, et al. Quality-of-life assessment before and after liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2005;37:2601–2614. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

