Two pools of Triton X-100-insoluble GABA(A) receptors are present in the brain, one associated to lipid rafts and another one to the post-synaptic GABAergic complex
- PMID: 17663755
- PMCID: PMC2766244
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04635.x
Two pools of Triton X-100-insoluble GABA(A) receptors are present in the brain, one associated to lipid rafts and another one to the post-synaptic GABAergic complex
Abstract
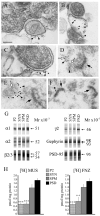
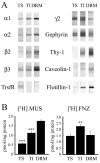
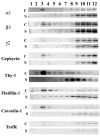
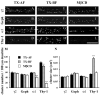
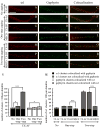
Rat forebrain synaptosomes were extracted with Triton X-100 at 4 degrees C and the insoluble material, which is enriched in post-synaptic densities (PSDs), was subjected to sedimentation on a continuous sucrose gradient. Two pools of Triton X-100-insoluble gamma-aminobutyric acid type-A receptors (GABA(A)Rs) were identified: (i) a higher-density pool (rho = 1.10-1.15 mg/mL) of GABA(A)Rs that contains the gamma2 subunit (plus alpha and beta subunits) and that is associated to gephyrin and the GABAergic post-synaptic complex and (ii) a lower-density pool (rho = 1.06-1.09 mg/mL) of GABA(A)Rs associated to detergent-resistant membranes (DRMs) that contain alpha and beta subunits but not the gamma2 subunit. Some of these GABA(A)Rs contain the delta subunit. Two pools of GABA(A)Rs insoluble in Triton X-100 at 4 degrees C were also identified in cultured hippocampal neurons: (i) a GABA(A)R pool that forms clusters that co-localize with gephyrin and remains Triton X-100-insoluble after cholesterol depletion and (ii) a GABA(A)R pool that is diffusely distributed at the neuronal surface that can be induced to form GABA(A)R clusters by capping with an anti-alpha1 GABA(A)R subunit antibody and that becomes solubilized in Triton X-100 at 4 degrees C after cholesterol depletion. Thus, there is a pool of GABA(A)Rs associated to lipid rafts that is non-synaptic and that has a subunit composition different from that of the synaptic GABA(A)Rs. Some of the lipid raft-associated GABA(A)Rs might be involved in tonic inhibition.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipid raft localization of GABA A receptor and Na+, K+-ATPase in discrete microdomain clusters in rat cerebellar granule cells.Neurochem Int. 2005 May;46(6):489-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2004.11.010. Neurochem Int. 2005. PMID: 15769551
-
alpha5 Subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors form clusters at GABAergic synapses in hippocampal cultures.Neuroreport. 2002 Dec 3;13(17):2355-8. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200212030-00037. Neuroreport. 2002. PMID: 12488826
-
Increased phosphorylation and redistribution of NMDA receptors between synaptic lipid rafts and post-synaptic densities following transient global ischemia in the rat brain.J Neurochem. 2005 Apr;93(1):186-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.03009.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 15773918
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor α subunits play a direct role in synaptic versus extrasynaptic targeting.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 10;287(33):27417-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.360461. Epub 2012 Jun 18. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22711532 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct properties of murine alpha 5 gamma-aminobutyric acid type a receptors revealed by biochemical fractionation and mass spectroscopy.J Neurosci Res. 2009 Jun;87(8):1737-47. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21991. J Neurosci Res. 2009. PMID: 19156871
Cited by
-
In vivo transgenic expression of collybistin in neurons of the rat cerebral cortex.J Comp Neurol. 2017 Apr 1;525(5):1291-1311. doi: 10.1002/cne.24137. Epub 2016 Nov 21. J Comp Neurol. 2017. PMID: 27804142 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of host factors involved in borna disease virus cell entry through a small interfering RNA functional genetic screen.J Virol. 2010 Apr;84(7):3562-75. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02274-09. Epub 2010 Jan 13. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20071576 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Dysregulation of Cholesterol Synthesis Underlies Hyposensitivity to GABA in the Ventral Tegmental Area During Acute Alcohol Withdrawal.Biol Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 1;95(3):275-285. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2023.07.018. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Biol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 37562519 Free PMC article.
-
The calcineurin inhibitor Ascomicin interferes with the early stage of the epileptogenic process induced by Latrunculin A microperfusion in rat hippocampus.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;9(5):654-67. doi: 10.1007/s11481-014-9558-9. Epub 2014 Aug 8. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25104570
-
Synapse biology in the 'circuit-age'-paths toward molecular connectomics.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017 Feb;42:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2016.12.004. Epub 2016 Dec 26. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28033531 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Becher A, White JA, McIlhinney RA. The gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor B, but not the metabotropic glutamate receptor type-1, associates with lipid rafts in the rat cerebellum. J Neurochem. 2001;79:787–795. - PubMed
-
- Besshoh S, Bawa D, Teves L, Wallace MC, Gurd JW. TevesIncreased phosphorylation and redistribution of NMDA receptors between synaptic lipid rafts and post-synaptic densities following transient global ischemia in the rat brain. J Neurochem. 2005;93:186–194. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Rose JK. Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipid- enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell. 1992;68:533–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

