Roles of amyloid beta-peptide-associated oxidative stress and brain protein modifications in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment
- PMID: 17664130
- PMCID: PMC2031860
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.05.037
Roles of amyloid beta-peptide-associated oxidative stress and brain protein modifications in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment
Abstract
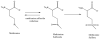
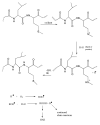
Oxidative stress has been implicated to play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of a number of diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, cancer, and ischemia, just to name a few. Alzheimer disease (AD) is an age-related neurodegenerative disorder that is recognized as the most common form of dementia. AD is histopathologically characterized by the presence of extracellular amyloid plaques, intracellular neurofibrillary tangles, the presence of oligomers of amyloid beta-peptide (Abeta), and synapse loss. In this review we discuss the role of Abeta in the pathogenesis of AD and also the use of redox proteomics to identify oxidatively modified brain proteins in AD and mild cognitive impairment. In addition, redox proteomics studies in in vivo models of AD centered around human Abeta(1-42) are discussed.
Figures



References
-
- Butterfield DA. Amyloid beta-peptide (1-42)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: implications for neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease brain. A review. Free Radic Res. 2002;36:1307–1313. - PubMed
-
- Butterfield DA, Castegna A, Lauderback CM, Drake J. Evidence that amyloid beta-peptide-induced lipid peroxidation and its sequelae in Alzheimer's disease brain contribute to neuronal death. Neurobiol Aging. 2002;23:655–664. - PubMed
-
- Butterfield DA, Drake J, Pocernich C, Castegna A. Evidence of oxidative damage in Alzheimer's disease brain: central role for amyloid beta-peptide. Trends Mol Med. 2001;7:548–554. - PubMed
-
- Butterfield DA, Lauderback CM. Lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation in Alzheimer's disease brain: potential causes and consequences involving amyloid beta-peptide-associated free radical oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;32:1050–1060. - PubMed
-
- Markesbery WR. Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer's disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 1997;23:134–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

