Ribosomal slowdown mediates translational arrest during cellular division
- PMID: 17664278
- PMCID: PMC2099241
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00798-07
Ribosomal slowdown mediates translational arrest during cellular division
Abstract
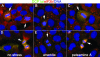
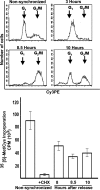
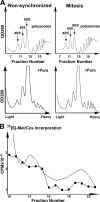
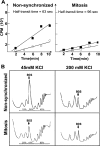
Global mRNA translation is transiently inhibited during cellular division. We demonstrate that mitotic cells contain heavy polysomes, but these are significantly less translationally active than polysomes in cycling cells. Several observations indicate that mitotic translational attenuation occurs during the elongation stage: (i) in cycling nonsynchronized cultures, only mitotic cells fail to assemble stress granules when treated with agents that inhibit translational initiation; (ii) mitotic cells contain fewer free 80S complexes, which are less sensitive to high salt disassembly; (iii) mitotic polysomes are more resistant to enforced disassembly using puromycin; and (iv) ribosome transit time increases during mitosis. Elongation slowdown guarantees that polysomes are retained even if initiation is inhibited at the same time. Stalling translating ribosomes during mitosis may protect mRNAs and allow rapid resumption of translation immediately upon entry into the G(1) phase.
Figures


References
-
- Bonneau, A. M., and N. Sonenberg. 1987. Involvement of the 24-kDa cap-binding protein in regulation of protein synthesis in mitosis. J. Biol. Chem. 262:11134-11139. - PubMed
-
- Bordeleau, M. E., R. Cencic, L. Lindqvist, M. Oberer, P. Northcote, G. Wagner, and J. Pelletier. 2006. RNA-mediated sequestration of the RNA helicase eIF4A by pateamine A inhibits translation initiation. Chem. Biol. 13:1287-1295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
