The neutrophil serine protease inhibitor serpinb1 preserves lung defense functions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
- PMID: 17664292
- PMCID: PMC2118684
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20070494
The neutrophil serine protease inhibitor serpinb1 preserves lung defense functions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
Abstract
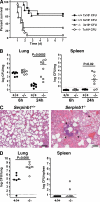
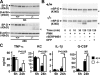
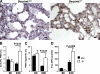
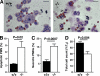
Neutrophil serine proteases (NSPs; elastase, cathepsin G, and proteinase-3) directly kill invading microbes. However, excess NSPs in the lungs play a central role in the pathology of inflammatory pulmonary disease. We show that serpinb1, an efficient inhibitor of the three NSPs, preserves cell and molecular components responsible for host defense against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. On infection, wild-type (WT) and serpinb1-deficient mice mount similar early responses, including robust production of cytokines and chemokines, recruitment of neutrophils, and initial containment of bacteria. However, serpinb1(-/-) mice have considerably increased mortality relative to WT mice in association with late-onset failed bacterial clearance. We found that serpinb1-deficient neutrophils recruited to the lungs have an intrinsic defect in survival accompanied by release of neutrophil protease activity, sustained inflammatory cytokine production, and proteolysis of the collectin surfactant protein-D (SP-D). Coadministration of recombinant SERPINB1 with the P. aeruginosa inoculum normalized bacterial clearance in serpinb1(-/-) mice. Thus, regulation of pulmonary innate immunity by serpinb1 is nonredundant and is required to protect two key components, the neutrophil and SP-D, from NSP damage during the host response to infection.
Figures


References
-
- Reeves, E.P., H. Lu, H.L. Jacobs, C.G. Messina, S. Bolsover, G. Gabella, E.O. Potma, A. Warley, J. Roes, and A.W. Segal. 2002. Killing activity of neutrophils is mediated through activation of proteases by K+ flux. Nature. 416:291–297. - PubMed
-
- Belaaouaj, A., K.S. Kim, and S.D. Shapiro. 2000. Degradation of outer membrane protein A in Escherichia coli killing by neutrophil elastase. Science. 289:1185–1188. - PubMed
-
- Belaaouaj, A., R. McCarthy, M. Baumann, Z. Gao, T.J. Ley, S.N. Abraham, and S.D. Shapiro. 1998. Mice lacking neutrophil elastase reveal impaired host defense against gram negative bacterial sepsis. Nat. Med. 4:615–618. - PubMed
-
- Tkalcevic, J., M. Novelli, M. Phylactides, J.P. Iredale, A.W. Segal, and J. Roes. 2000. Impaired immunity and enhanced resistance to endotoxin in the absence of neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G. Immunity. 12:201–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

