influence of TEM-1 beta-lactamase on the pharmacodynamic activity of simulated total versus free-drug serum concentrations of cefditoren (400 milligrams) versus amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (2,000/125 milligrams) against Haemophilus influenzae strains exhibiting an N526K mutation in the ftsI gene
- PMID: 17664320
- PMCID: PMC2043252
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01530-06
influence of TEM-1 beta-lactamase on the pharmacodynamic activity of simulated total versus free-drug serum concentrations of cefditoren (400 milligrams) versus amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (2,000/125 milligrams) against Haemophilus influenzae strains exhibiting an N526K mutation in the ftsI gene
Abstract
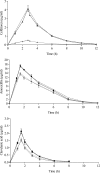
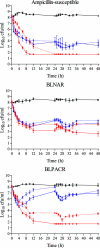
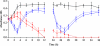
The aim of this study was to explore bactericidal activity of total and free serum simulated concentrations after the oral administration of cefditoren (400 mg, twice daily [bid]) versus the oral administration of amoxicillin-clavulanic acid extended release formulation (2,000/125 mg bid) against Haemophilus influenzae. A computerized pharmacodynamic simulation was performed, and colony counts and beta-lactamase activity were determined over 48 h. Three strains were used: ampicillin-susceptible, beta-lactamase-negative ampicillin-resistant (BLNAR) (also resistant to amoxicillin-clavulanic acid) and beta-lactamase-positive amoxicillin-clavulanic acid-resistant (BLPACR) strains, with cefditoren MICs of < or =0.12 microg/ml and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid MICs of 2, 8, and 8 microg/ml, respectively. Against the ampicillin-susceptible and BLNAR strains, bactericidal activity (> or =3 log(10) reduction) was obtained from 6 h on with either total and free cefditoren or amoxicillin-clavulanic acid. Against the BLPACR strain, free cefditoren showed bactericidal activity from 8 h on. In amoxicillin-clavulanic acid simulations the increase in colony counts from 4 h on occurred in parallel with the increase in beta-lactamase activity for the BLPACR strain. Since both BLNAR and BLPACR strains exhibited the same MIC, this was due to the significantly lower (P < or = 0.012) amoxicillin concentrations from 4 h on in simulations with beta-lactamase positive versus negative strains, thus decreasing the time above MIC (T>MIC). From a pharmacodynamic point of view, the theoretical amoxicillin T>MIC against strains with elevated ampicillin/amoxicillin-clavulanic acid MICs should be considered with caution since the presence of beta-lactamase inactivates the antibiotic, thus rendering inaccurate theoretical calculations. The experimental bactericidal activity of cefditoren is maintained over the dosing interval regardless of the presence of a mutation in the ftsI gene or beta-lactamase production.
Figures

References
-
- Andrews, J. M. 1999. Microbiological assays, p. 35-44. In D. S. Reeves, R. Wise, J. M. Andrews, and L. O. White (ed.), Clinical antimicrobial assays. Oxford University Press, Oxford, United Kingdom.
-
- Ball, P., F. Baquero, O. Cars, T. File, J. Garau, K. Klugman, D. E. Low, E. Rubinstein, R. Wise, et al. 2002. Antibiotic therapy of community respiratory tract infections: strategies for optimal outcomes and minimized resistance emergence. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 49:31-40. - PubMed
-
- Blaser, J. 1985. In-vitro model for simultaneous simulation of the serum kinetics of two drugs with different half-lives. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 15(Suppl. A):125-130. - PubMed
-
- Cafini, F., L. Aguilar, N. Gonzalez, M. J. Gimenez, M. Torrico, L. Alou, D. Sevillano, P. Vallejo, and J. Prieto. 2007. In vitro effect of the presence of human albumin or human serum on the bactericidal activity of daptomycin against strains with the main resistance phenotypes in gram-positives. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 59:1185-1189. - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2005. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; fifteenth informational supplement. CLSI/NCCLS document M100-S15. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

