Robust expansion of human hepatocytes in Fah-/-/Rag2-/-/Il2rg-/- mice
- PMID: 17664939
- PMCID: PMC3404624
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt1326
Robust expansion of human hepatocytes in Fah-/-/Rag2-/-/Il2rg-/- mice
Abstract
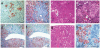
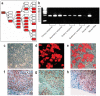
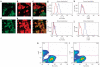
Mice that could be highly repopulated with human hepatocytes would have many potential uses in drug development and research applications. The best available model of liver humanization, the uroplasminogen-activator transgenic model, has major practical limitations. To provide a broadly useful hepatic xenorepopulation system, we generated severely immunodeficient, fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (Fah)-deficient mice. After pretreatment with a urokinase-expressing adenovirus, these animals could be highly engrafted (up to 90%) with human hepatocytes from multiple sources, including liver biopsies. Furthermore, human cells could be serially transplanted from primary donors and repopulate the liver for at least four sequential rounds. The expanded cells displayed typical human drug metabolism. This system provides a robust platform to produce high-quality human hepatocytes for tissue culture. It may also be useful for testing the toxicity of drug metabolites and for evaluating pathogens dependent on human liver cells for replication.
Figures



Comment in
-
A human hepatocyte factory.Nat Biotechnol. 2007 Aug;25(8):871-2. doi: 10.1038/nbt0807-871. Nat Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17687361 No abstract available.
References
-
- Brandon EF, Raap CD, Meijerman I, Beijnen JH, Schellens JH. An update on in vitro test methods in human hepatic drug biotransformation research: pros and cons. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003;189:233–246. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Lechon MJ, Donato MT, Castell JV, Jover R. Human hepatocytes as a tool for studying toxicity and drug metabolism. Curr. Drug Metab. 2003;4:292–312. - PubMed
-
- Runge D, Michalopoulos GK, Strom SC, Runge DM. Recent advances in human hepatocyte culture systems. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000;274:1–3. - PubMed
-
- Cascio SM. Novel strategies for immortalization of human hepatocytes. Artif. Organs. 2001;25:529–538. - PubMed
-
- Dandri M, et al. Chronic infection with hepatitis B viruses and antiviral drug evaluation in uPA mice after liver repopulation with tupaia hepatocytes. J. Hepatol. 2005;42:54–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

