Tool use changes multisensory interactions in seconds: evidence from the crossmodal congruency task
- PMID: 17665178
- PMCID: PMC2084481
- DOI: 10.1007/s00221-007-1060-7
Tool use changes multisensory interactions in seconds: evidence from the crossmodal congruency task
Abstract
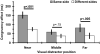
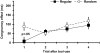
Active tool use in human and non-human primates has been claimed to alter the neural representations of multisensory peripersonal space. To date, most studies suggest that a short period of tool use leads to an expansion or elongation of these spatial representations, which lasts several minutes after the last tool use action. However, the possibility that multisensory interactions also change on a much shorter time scale following or preceding individual tool use movements has not yet been investigated. We measured crossmodal (visual-tactile) congruency effects as an index of multisensory integration during two tool use tasks. In the regular tool use task, the participants used one of two tools in a spatiotemporally predictable sequence after every fourth crossmodal congruency trial. In the random tool use task, the required timing and spatial location of the tool use task varied unpredictably. Multisensory integration effects increased as a function of the number of trials since tool use in the regular tool use group, but remained relatively constant in the random tool use group. The spatial distribution of these multisensory effects, however, was unaffected by tool use predictability, with significant spatial interactions found only near the hands and at the tips of the tools. These data suggest that endogenously preparing to use a tool enhances visual-tactile interactions near the tools. Such enhancements are likely due to the increased behavioural relevance of visual stimuli as each tool use action is prepared before execution.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Tool-use: capturing multisensory spatial attention or extending multisensory peripersonal space?Cortex. 2007 Apr;43(3):469-89. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(08)70471-4. Cortex. 2007. PMID: 17533769 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) for patellofemoral pain syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 12;12(12):CD011289. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011289.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29231243 Free PMC article.
-
Reading aids for adults with low vision.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 17;4(4):CD003303. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003303.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29664159 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Peripersonal space in the front, rear, left and right directions for audio-tactile multisensory integration.Sci Rep. 2021 May 28;11(1):11303. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90784-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34050213 Free PMC article.
-
The Embodiment of Objects: Review, Analysis, and Future Directions.Front Neurosci. 2019 Dec 13;13:1332. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01332. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31920499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripersonal space around the upper and the lower limbs.Exp Brain Res. 2022 Aug;240(7-8):2039-2050. doi: 10.1007/s00221-022-06387-7. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Exp Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 35727366 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of auditory peripersonal space by approaching and receding sources moving in discrete trajectories.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2025 Oct;87(7):2165-2183. doi: 10.3758/s13414-025-03071-0. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2025. PMID: 40474049
-
Haptic over visual information in the distribution of visual attention after tool-use in near and far space.Exp Brain Res. 2015 Oct;233(10):2977-88. doi: 10.1007/s00221-015-4368-8. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Exp Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26126805
References
-
- Ackroyd K, Riddoch MJ, Humphreys GW, Nightingale S, Townsend S. Widening the sphere of influence: Using a tool to extend extrapersonal visual space in a patient with severe neglect. Neurocase. 2002;8:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Berti A, Frassinetti F. When far becomes near: Remapping of space by tool use. J Cogn Neurosci. 2000;12:415–420. - PubMed
-
- Bonifazi S, Farnè A, Rinaldesi L, Làdavas E. Dynamic size-change of peri-hand space through tool-use: Spatial extension or shift of the multisensory area? J Neuropsychol. 2007;1:101–114. - PubMed
-
- Costantini M, Bueti D, Pazzaglia M, Aglioti SM. Temporal dynamics of visuo-tactile extinction within and between hemispaces. Neuropsychol. 2007;21:242–250. - PubMed
-
- Danckert J, Ferber S. Revisiting unilateral neglect. Neuropsychologia. 2006;44:987–1006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

