Alcohol use in adolescent twins and affiliation with substance using peers
- PMID: 17665304
- PMCID: PMC2905232
- DOI: 10.1007/s10802-007-9161-0
Alcohol use in adolescent twins and affiliation with substance using peers
Abstract
Affiliation with substance using peers is one of the strongest predictors of adolescent alcohol use. This association is typically interpreted causally: peers who drink incite their friends to drink. This association may be complicated by uncontrolled genetic and environmental confounds because teens with familial predispositions for adolescent substance use may be more likely to select into social networks where drinking is common. We test this alternative hypothesis using a sample of 1,820 twin and sibling pairs, and their same-sex best friends, from three waves of the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health. Across all three waves, peer report of substance use did not influence adolescent alcohol use when genetic and shared environmental predispositions for drinking were considered. The association between alcohol use and peer behavior may be a spurious association attributable to a shared genetic liability to drink alcohol and associate with peers who drink alcohol.
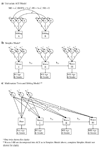
Figures
References
-
- Allison PD. Missing data. Sage university papers series on quantitative applications in the social sciences, 07– 136. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 2002.
-
- Bauman KE, Ennett ST. On the importance of peer influence for adolescent drug use: Commonly neglected considerations. Addiction. 1996;91(2):185–198. - PubMed
-
- Bentler PM. Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin. 1990;107:238–246. - PubMed
-
- Berkowitz WR. Perceived height, personality, and friendship choice. Psychological Reports. 1969;24(2):373–374. - PubMed
-
- Byrne BM, Shavelson RJ, Muthén B. Testing for the equivalence of factor covariance and mean structures: The issue of partial measurement invariance. Psychological Bulletin. 1989;105(3):456–466.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical