Pathogenetic and prognostic significance of altered coagulation and fibrinolysis in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome
- PMID: 17667242
- PMCID: PMC2764536
- DOI: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000221922.08878.49
Pathogenetic and prognostic significance of altered coagulation and fibrinolysis in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome
Abstract
Objective: The coagulation and inflammatory cascades may be linked in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. However, direct evidence for the contribution of abnormalities in coagulation and fibrinolysis proteins to outcomes in patients with acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome is lacking.
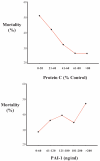
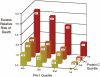
Design: Retrospective measurement of plasma levels of protein C and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in plasma samples that were collected prospectively as part of a large multicenter clinical trial. The primary outcome was hospital mortality. To evaluate the potential additive value of abnormalities of these biomarkers, the excess relative risk of death was calculated for each combination of quartiles of protein-C and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 levels.
Setting: Ten university medical centers.
Patients: The study included 779 patients from a multicenter clinical trial of a protective ventilatory strategy in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome and 99 patients with acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema, as well as ten normal controls.
Measurements and main results: Compared with plasma from controls and patients with acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema, baseline protein-C levels were low and baseline plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 levels were elevated in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. By multivariate analysis, lower protein C and higher plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 were strong independent predictors of mortality, and ventilator-free and organ-failure-free days. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and protein C had a synergistic interaction for the risk of death.
Conclusions: Early acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome is characterized by decreased plasma levels of protein C and increased plasma levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 that are independent risk factors for mortality and adverse clinical outcomes. Measurement of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and protein-C levels may be useful to identify those at highest risk of adverse clinical outcomes for the development of new therapies.
Figures
Comment in
-
Is there an association between hemostatic abnormalities and the outcome of acute lung injury?Crit Care Med. 2007 Aug;35(8):1980-2. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000277253.47121.6B. Crit Care Med. 2007. PMID: 17667245 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA. Medical progress: The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1334–1349. - PubMed
-
- Brower RG, Ware LB, Berthiaume Y, et al. Treatment of ARDS. Chest. 2001;120:1347–1367. - PubMed
-
- The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1301–1308. - PubMed
-
- Brun-Buisson C, Minelli C, Bertolini G, et al. Epidemiology and outcome of acute lung injury in European intensive care units. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30:51–61. - PubMed
-
- Idell S, Gonzalez K, Bradford H, et al. Procoagulant activity in bronchoalveolar lavage in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987;136:1466–1474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N0-1 HR 46059/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR046054/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N0-1 HR 46055/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N0-1 HR 46060/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL074005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N0-1 HR 46058/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N0-1 HR 46054/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL051856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL004201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N0-1 HR 46061/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 04201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL74005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N0-1 HR 46063/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N0-1 HR 46056/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 70521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 51856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N0-1 HR 46057/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N0-1 HR 46062/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL051856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N0-1 HR 46064/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL070521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL081332/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL081332/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

