Cyclooxygenase-2 independent effects of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on oxidative stress and intracellular glutathione content in normal and malignant human B-cells
- PMID: 17668203
- PMCID: PMC11031111
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-007-0374-4
Cyclooxygenase-2 independent effects of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on oxidative stress and intracellular glutathione content in normal and malignant human B-cells
Abstract
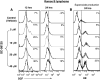
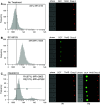
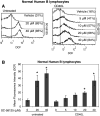
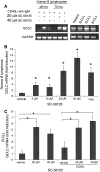
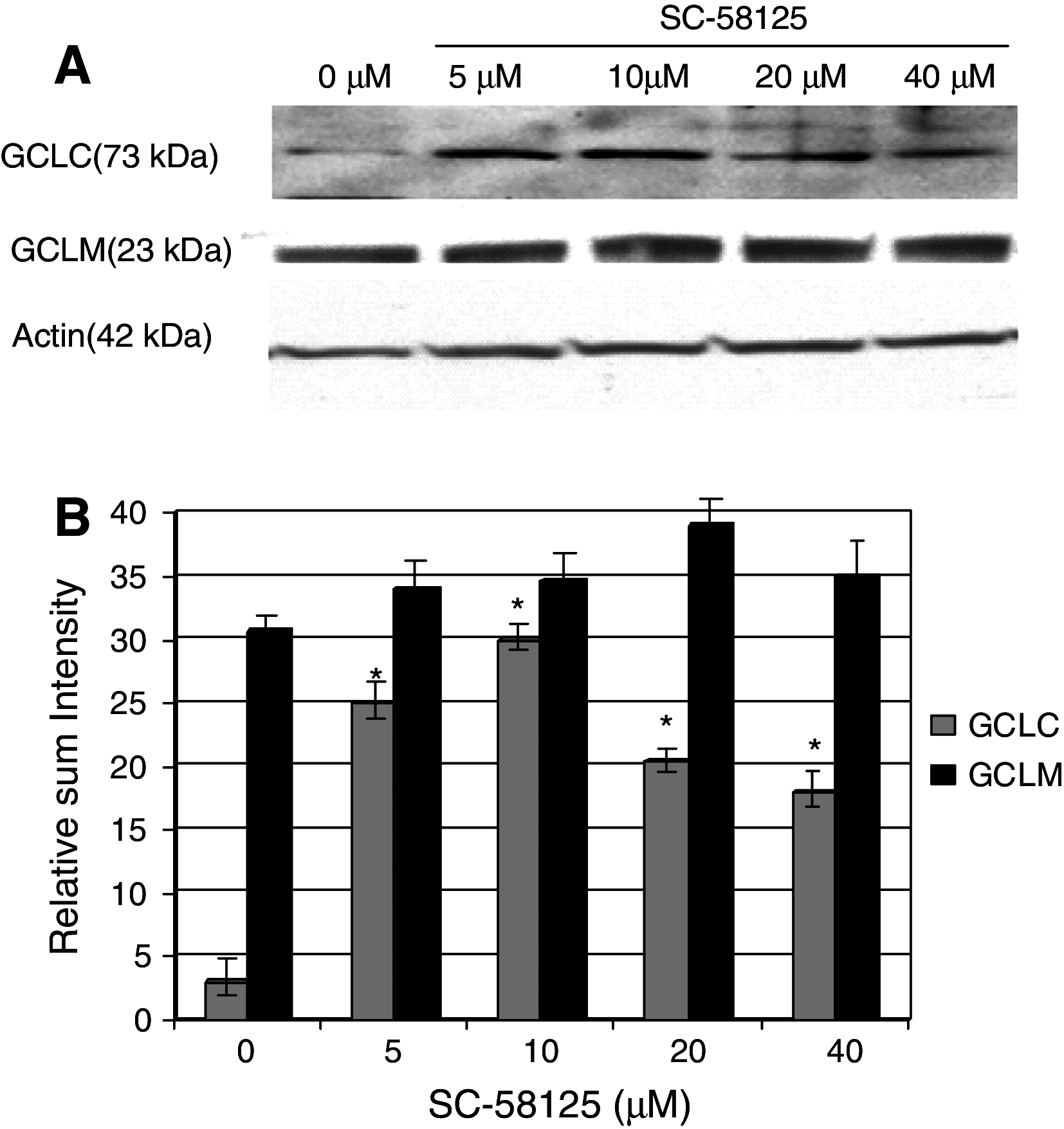
We recently reported that inhibition of Cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2) reduced human B-CLL proliferation and survival. Herein, we investigated the mechanisms whereby small molecule Cox-2 selective inhibitors, SC-58125 (a Celebrex analog) and CAY10404 blunt survival of human B-cell lymphomas and chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cells. SC-58125 and OSU03012 (a Celebrex analog that lacks Cox-2 inhibitory activity) both decreased intracellular glutathione (GSH) content in malignant human B-cells, as well as in Cox-2 deficient mouse B-cells. This new finding supports Cox-2 independent effects of SC-58125. Interestingly, SC-58125 also significantly increased B-cell reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, suggesting that ROS are a pathway that reduces malignant cell survival. Addition of GSH ethyl ester protected B lymphomas from the increased mitochondrial membrane permeability and reduced survival induced by SC-58125. Moreover, the SC-58125-mediated GSH depletion resulted in elevated steady-state levels of the glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit mRNA and protein. These new findings of increased ROS and diminished GSH levels following SC-58125 exposure support novel mechanisms whereby a Cox-2 selective inhibitor reduces malignant B-cell survival. These observations also support the concept that certain Cox-2 selective inhibitors may have therapeutic value in combination with other drugs to kill malignant B lineage cells.
Figures


References
-
- Singh B, Berry JA, Shoher A, Ramakrishnan V, Lucci A. COX-2 overexpression increases motility and invasion of breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2005;26:1393–1399. - PubMed
-
- Nakao S, Kuwano T, Tsutsumi-Miyahara C, Ueda S, Kimura YN, Hamano S, Sonoda KH, Saijo Y, Nukiwa T, Strieter RM, Ishibashi T, Kuwano M, Ono M. Infiltration of COX-2-expressing macrophages is a prerequisite for IL-1beta-induced neovascularization and tumor growth. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:2979–2991. doi: 10.1172/JCI23298. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

