Permanent neonatal diabetes caused by dominant, recessive, or compound heterozygous SUR1 mutations with opposite functional effects
- PMID: 17668386
- PMCID: PMC1950816
- DOI: 10.1086/519174
Permanent neonatal diabetes caused by dominant, recessive, or compound heterozygous SUR1 mutations with opposite functional effects
Abstract
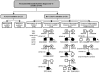
Heterozygous activating mutations in the KCNJ11 gene encoding the pore-forming Kir6.2 subunit of the pancreatic beta cell K(ATP) channel are the most common cause of permanent neonatal diabetes (PNDM). Patients with PNDM due to a heterozygous activating mutation in the ABCC8 gene encoding the SUR1 regulatory subunit of the K(ATP) channel have recently been reported. We studied a cohort of 59 patients with permanent diabetes who received a diagnosis before 6 mo of age and who did not have a KCNJ11 mutation. ABCC8 gene mutations were identified in 16 of 59 patients and included 8 patients with heterozygous de novo mutations. A recessive mode of inheritance was observed in eight patients with homozygous, mosaic, or compound heterozygous mutations. Functional studies of selected mutations showed a reduced response to ATP consistent with an activating mutation that results in reduced insulin secretion. A novel mutational mechanism was observed in which a heterozygous activating mutation resulted in PNDM only when a second, loss-of-function mutation was also present.
Figures



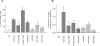

References
Web Resources
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for ABCC8 [accession number NM_000352.2 incorporating the alternate exon 17: L78208, L78224], Kir6.2 [accession number NM_000525 with E23 and I337], and SUR1 [accession number NM_000352 incorporating the alternate exon 17; also L78208 and L78224])
-
- International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes, http://www.ispad.org/
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for KCNJ11, ABCC8, congenital hyperinsulinism, and PNDM)
References
-
- Gloyn AL, Pearson ER, Antcliff JF, Proks P, Bruining GJ, Slingerland AS, Howard N, Srinivasan S, Silva JM, Molnes J, et al (2004) Activating mutations in the gene encoding the ATP-sensitive potassium-channel subunit Kir6.2 and permanent neonatal diabetes. N Engl J Med 350:1838–184910.1056/NEJMoa032922 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

