Human microRNA-155 on chromosome 21 differentially interacts with its polymorphic target in the AGTR1 3' untranslated region: a mechanism for functional single-nucleotide polymorphisms related to phenotypes
- PMID: 17668390
- PMCID: PMC1950808
- DOI: 10.1086/519979
Human microRNA-155 on chromosome 21 differentially interacts with its polymorphic target in the AGTR1 3' untranslated region: a mechanism for functional single-nucleotide polymorphisms related to phenotypes
Abstract
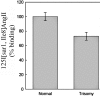
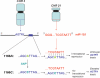
Animal microRNAs (miRNAs) regulate gene expression through base pairing to their targets within the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of protein-coding genes. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located within such target sites can affect miRNA regulation. We mapped annotated SNPs onto a collection of experimentally supported human miRNA targets. Of the 143 experimentally supported human target sites, 9 contain 12 SNPs. We further experimentally investigated one of these target sites for hsa-miR-155, within the 3' UTR of the human AGTR1 gene that contains SNP rs5186. Using reporter silencing assays, we show that hsa-miR-155 down-regulates the expression of only the 1166A, and not the 1166C, allele of rs5186. Remarkably, the 1166C allele has been associated with hypertension in many studies. Thus, the 1166C allele may be functionally associated with hypertension by abrogating regulation by hsa-miR-155, thereby elevating AGTR1 levels. Since hsa-miR-155 is on chromosome 21, we hypothesize that the observed lower blood pressure in trisomy 21 is partially caused by the overexpression of hsa-miR-155 leading to allele-specific underexpression of AGTR1. Indeed, we have shown in fibroblasts from monozygotic twins discordant for trisomy 21 that levels of AGTR1 protein are lower in trisomy 21.
Figures

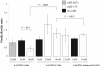

References
Web Resources
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for hypertension)
-
- TarBase, http://diana.pcbi.upenn.edu/tarbase (for the database of experimentally supported targets)
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

