Control of matrix metalloproteinase catalytic activity
- PMID: 17669641
- PMCID: PMC2246078
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2007.07.001
Control of matrix metalloproteinase catalytic activity
Abstract
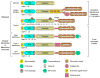
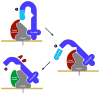
As their name implies, MMPs were first described as proteases that degrade extracellular matrix proteins, such as collagens, elastin, proteoglycans, and laminins. However, studies of MMP function in vivo have revealed that these proteinases act on a variety of extracellular protein substrates, often to activate latent forms of effector proteins, such as antimicrobial peptides and cytokines, or to alter protein function, such as shedding of cell-surface proteins. Because their substrates are diverse, MMPs are involved in variety of homeostatic functions, such as bone remodeling, wound healing, and several aspects of immunity. However, MMPs are also involved in a number of pathological processes, such as tumor progression, fibrosis, chronic inflammation, tissue destruction, and more. A key step in regulating MMP proteolysis is the conversion of the zymogen into an active proteinase. Several proMMPs are activated in the secretion pathway by furin proprotein convertases, but for most the activation mechanisms are largely not known. In this review, we discuss both authentic and potential mechanisms of proMMP activation.
Figures

References
-
- Åbrink M, Grujic M, Pejler G. Serglycin is essential for maturation of mast cell secretory granule. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:40897–40905. - PubMed
-
- Almeida PC, I, Nantes L, Chaga JR, Rizzi CCA, Faljoni-Alario A, Carmona E, Juliano L, Nader HB, Tersariol ILS. Cathepsin B activity regulation : Heparin-like glycoaminoglycans protect human cathepsin B from alkaline pH-induced inactivation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:944–951. - PubMed
-
- Balbin M, Fueyo A, Knauper V, Lopez JM, Alvarez J, Sanchez LM, Quesada V, Bordallo J, Murphy G, Lopez-Otin C. Identification and enzymatic characterization of two diverging murine counterparts of human interstitial collagenase (MMP-1) expressed at sites of embryo implantation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:10253–62. - PubMed
-
- Berglin L, Sarman S, van der Ploeg I, Steen B, Ming Y, Itohara S, Seregard S, Kvanta A. Reduced choroidal neovascular membrane formation in matrix metalloproteinase-2-deficient mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:403–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

