Local selection rules that can determine specific pathways of DNA unknotting by type II DNA topoisomerases
- PMID: 17670794
- PMCID: PMC1976442
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm532
Local selection rules that can determine specific pathways of DNA unknotting by type II DNA topoisomerases
Abstract
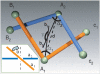
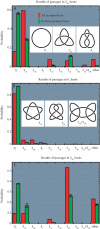
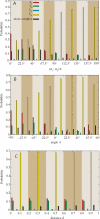
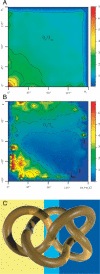
We performed numerical simulations of DNA chains to understand how local geometry of juxtaposed segments in knotted DNA molecules can guide type II DNA topoisomerases to perform very efficient relaxation of DNA knots. We investigated how the various parameters defining the geometry of inter-segmental juxtapositions at sites of inter-segmental passage reactions mediated by type II DNA topoisomerases can affect the topological consequences of these reactions. We confirmed the hypothesis that by recognizing specific geometry of juxtaposed DNA segments in knotted DNA molecules, type II DNA topoisomerases can maintain the steady-state knotting level below the topological equilibrium. In addition, we revealed that a preference for a particular geometry of juxtaposed segments as sites of strand-passage reaction enables type II DNA topoisomerases to select the most efficient pathway of relaxation of complex DNA knots. The analysis of the best selection criteria for efficient relaxation of complex knots revealed that local structures in random configurations of a given knot type statistically behave as analogous local structures in ideal geometric configurations of the corresponding knot type.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Theoretical models of DNA topology simplification by type IIA DNA topoisomerases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jun;37(10):3125-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp250. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19383879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tightening of DNA knots by supercoiling facilitates their unknotting by type II DNA topoisomerases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Mar 1;108(9):3608-11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1016150108. Epub 2011 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21321228 Free PMC article.
-
Topological information embodied in local juxtaposition geometry provides a statistical mechanical basis for unknotting by type-2 DNA topoisomerases.J Mol Biol. 2006 Aug 11;361(2):268-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.06.005. Epub 2006 Jun 19. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16842819
-
DNA supercoiling inhibits DNA knotting.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Sep;36(15):4956-63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn467. Epub 2008 Jul 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18658246 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical basis for the interactions of type I and type II topoisomerases with DNA.Pharmacol Ther. 1989;41(1-2):223-41. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90108-3. Pharmacol Ther. 1989. PMID: 2540496 Review.
Cited by
-
Action at hooked or twisted-hooked DNA juxtapositions rationalizes unlinking preference of type-2 topoisomerases.J Mol Biol. 2010 Jul 30;400(5):963-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.05.007. Epub 2010 May 10. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20460130 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical models of DNA topology simplification by type IIA DNA topoisomerases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jun;37(10):3125-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp250. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19383879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA catenation maintains structure of human metaphase chromosomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Dec;40(22):11428-34. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks931. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 23066100 Free PMC article.
-
DNA supercoiling and its role in DNA decatenation and unknotting.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Apr;38(7):2119-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1161. Epub 2009 Dec 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20026582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinetic pathways of topology simplification by Type-II topoisomerases in knotted supercoiled DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 10;47(1):69-84. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1174. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30476194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maxwell A, Costenaro L, Mitelheiser S, Bates AD. Coupling ATP hydrolysis to DNA strand passage in type IIA DNA topoisomerases. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005;33:1460–1464. - PubMed
-
- Bates AD, Maxwell A. DNA Topology. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2005.

