Stable reduction of CCR5 by RNAi through hematopoietic stem cell transplant in non-human primates
- PMID: 17670939
- PMCID: PMC1941789
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705474104
Stable reduction of CCR5 by RNAi through hematopoietic stem cell transplant in non-human primates
Abstract
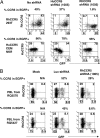
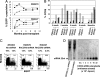
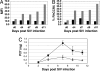
RNAi is a powerful method for suppressing gene expression that has tremendous potential for therapeutic applications. However, because endogenous RNAi plays a role in normal cellular functions, delivery and expression of siRNAs must be balanced with safety. Here we report successful stable expression in primates of siRNAs directed to chemokine (c-c motif) receptor 5 (CCR5) introduced through CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell transplant. After hematopoietic reconstitution, to date 14 months after transplant, we observe stably marked lymphocytes expressing siRNAs and consistent down-regulation of chemokine (c-c motif) receptor 5 expression. The marked cells are less susceptible to simian immunodeficiency virus infection ex vivo. These studies provide a successful demonstration that siRNAs can be used together with hematopoietic stem cell transplant to stably modulate gene expression in primates and potentially treat blood diseases such as HIV-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Rubinson DA, Dillon CP, Kwiatkowski AV, Sievers C, Yang L, Kopinja J, Rooney DL, Ihrig MM, McManus MT, Gertler FB, et al. Nat Genet. 2003;33:401–406. - PubMed
-
- Grimm D, Streetz KL, Jopling CL, Storm TA, Pandey K, Davis CR, Marion P, Salazar F, Kay MA, et al. Nature. 2006;441:537–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

