Cell type-specific tuning of hippocampal interneuron firing during gamma oscillations in vivo
- PMID: 17670965
- PMCID: PMC6673067
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1685-07.2007
Cell type-specific tuning of hippocampal interneuron firing during gamma oscillations in vivo
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2009 Mar 4;29(9):3009
Abstract
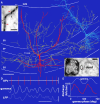
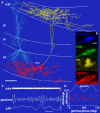
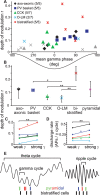
Cortical gamma oscillations contribute to cognitive processing and are thought to be supported by perisomatic-innervating GABAergic interneurons. We performed extracellular recordings of identified interneurons in the hippocampal CA1 area of anesthetized rats, revealing that the firing patterns of five distinct interneuron types are differentially correlated to spontaneous gamma oscillations. The firing of bistratified cells, which target dendrites of pyramidal cells coaligned with the glutamatergic input from hippocampal area CA3, is strongly phase locked to field gamma oscillations. Parvalbumin-expressing basket, axo-axonic, and cholecystokinin-expressing interneurons exhibit moderate gamma modulation, whereas the spike timing of distal dendrite-innervating oriens-lacunosum moleculare interneurons is not correlated to field gamma oscillations. Cholecystokinin-expressing interneurons fire earliest in the gamma cycle, a finding that is consistent with their suggested function of thresholding individual pyramidal cells. Furthermore, we show that field gamma amplitude correlates with interneuronal spike-timing precision and firing rate. Overall, our recordings suggest that gamma synchronization in vivo is assisted by temporal- and domain-specific GABAergic inputs to pyramidal cells and is initiated in pyramidal cell dendrites in addition to somata and axon initial segments.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez FJ, Villalba RM, Carr PA, Grandes P, Somohano PM. Differential distribution of metabotropic glutamate receptors 1a, 1b, and 5 in the rat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 2000;422:464–487. - PubMed
-
- Bacci A, Huguenard JR. Enhancement of spike-timing precision by autaptic transmission in neocortical inhibitory interneurons. Neuron. 2006;49:119–130. - PubMed
-
- Bartos M, Vida I, Jonas P. Synaptic mechanisms of synchronized gamma oscillations in inhibitory interneuron networks. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:45–56. - PubMed
-
- Baude A, Bleasdale C, Dalezios Y, Somogyi P, Klausberger T. Immunoreactivity for the GABAA receptor α1 subunit, somatostatin and connexin36 distinguishes axoaxonic, basket, and bistratified interneurons of the rat hippocampus. Cereb Cortex. 2007 in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
