Subventricular zone stem cells are heterogeneous with respect to their embryonic origins and neurogenic fates in the adult olfactory bulb
- PMID: 17670975
- PMCID: PMC6331046
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0476-07.2007
Subventricular zone stem cells are heterogeneous with respect to their embryonic origins and neurogenic fates in the adult olfactory bulb
Abstract
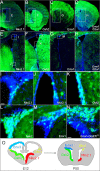
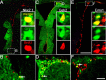
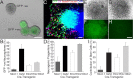
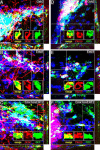
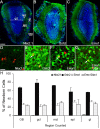
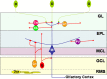
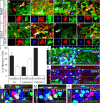
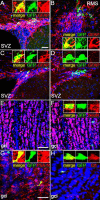
We determined the embryonic origins of adult forebrain subventricular zone (SVZ) stem cells by Cre-lox fate mapping in transgenic mice. We found that all parts of the telencephalic neuroepithelium, including the medial ganglionic eminence and lateral ganglionic eminence (LGE) and the cerebral cortex, contribute multipotent, self-renewing stem cells to the adult SVZ. Descendants of the embryonic LGE and cortex settle in ventral and dorsal aspects of the dorsolateral SVZ, respectively. Both populations contribute new (5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine-labeled) tyrosine hydroxylase- and calretinin-positive interneurons to the adult olfactory bulb. However, calbindin-positive interneurons in the olfactory glomeruli were generated exclusively by LGE-derived stem cells. Thus, different SVZ stem cells have different embryonic origins, colonize different parts of the SVZ, and generate different neuronal progeny, suggesting that some aspects of embryonic patterning are preserved in the adult SVZ. This could have important implications for the design of endogenous stem cell-based therapies in the future.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Lim DA. For the long run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron. 2004;41:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Anthony TE, Klein C, Fishell G, Heintz N. Radial glia serve as neuronal progenitors in all regions of the central nervous system. Neuron. 2004;41:881–890. - PubMed
-
- Bedard A, Parent A. Evidence of newly generated neurons in the human olfactory bulb. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2004;151:159–168. - PubMed
-
- Cao BJ, Li Y. Reduced anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in Emx1 homozygous mutant mice. Brain Res. 2002;937:32–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
