Use of the novel Plk1 inhibitor ZK-thiazolidinone to elucidate functions of Plk1 in early and late stages of mitosis
- PMID: 17671160
- PMCID: PMC1995727
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-05-0517
Use of the novel Plk1 inhibitor ZK-thiazolidinone to elucidate functions of Plk1 in early and late stages of mitosis
Abstract
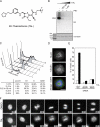
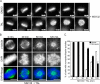
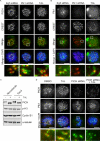
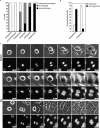
Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is a key regulator of mitotic progression and cell division in eukaryotes. It is highly expressed in tumor cells and considered a potential target for cancer therapy. Here, we report the discovery and application of a novel potent small-molecule inhibitor of mammalian Plk1, ZK-Thiazolidinone (TAL). We have extensively characterized TAL in vitro and addressed TAL specificity within cells by studying Plk1 functions in sister chromatid separation, centrosome maturation, and spindle assembly. Moreover, we have used TAL for a detailed analysis of Plk1 in relation to PICH and PRC1, two prominent interaction partners implicated in spindle assembly checkpoint function and cytokinesis, respectively. Specifically, we show that Plk1, when inactivated by TAL, spreads over the arms of chromosomes, resembling the localization of its binding partner PICH, and that both proteins are mutually dependent on each other for correct localization. Finally, we show that Plk1 activity is essential for cleavage furrow formation and ingression, leading to successful cytokinesis.
Figures




References
-
- Andrews C., III, et al. Thiophene compounds. International patent. WO2004/014899. 2004.
-
- Barr F. A., Sillje H.H.W., Nigg E. A. Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004;5:429–441. - PubMed
-
- Baumman C., Körner R., Hofmann K., Nigg E. A. PICH, a centromere-associated SNF2 family ATPase, is regulated by Plk1 and required for the spindle checkpoint. Cell. 2007;128:101–114. - PubMed
-
- Bearss D., Vankayalapati H., Grand C. Inhibitors of polo-like kinase-1. International patent. WO2006/124996. 2006.
-
- Berdnik D., Knoblich J. Drosophila Aurora-A is required for centrosome maturation and actin-dependent asymmetric protein localization during mitosis. Curr. Biol. 2002;12:640–647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

