Delayed immune reconstitution after cord blood transplantation is characterized by impaired thymopoiesis and late memory T-cell skewing
- PMID: 17671230
- PMCID: PMC2234787
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-092130
Delayed immune reconstitution after cord blood transplantation is characterized by impaired thymopoiesis and late memory T-cell skewing
Abstract
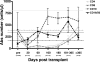
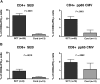
Advances in immune assessment, including the development of T-cell receptor excision circle (TREC) assays of thymopoiesis, cytokine-flow cytometry assays of T-cell function, and higher-order phenotyping of T-cell maturation subsets have improved our understanding of T-cell homeostasis. Limited data exist using these methods to characterize immune recovery in adult cord blood (CB) transplant recipients, in whom infection is a leading cause of mortality. We now report the results of a single-center prospective study of T-cell immune recovery after cord blood transplantation (CBT) in a predominantly adult population. Our primary findings include the following: (1) Prolonged T lymphopenia and compensatory expansion of B and natural killer (NK) cells was evident; (2) CB transplant recipients had impaired functional recovery, although we did observe posttransplantation de novo T-cell responses to cytomegalovirus (CMV) in a subset of patients; (3) Thymopoietic failure characterized post-CBT immune reconstitution, in marked contrast to results in other transplant recipients; and (4) Thymopoietic failure was associated with late memory T-cell skewing. Our data suggest that efforts to improve outcomes in adult CB transplant recipients should be aimed at optimizing T-cell immune recovery. Strategies that improve the engraftment of lymphoid precursors, protect the thymus during pretransplant conditioning, and/or augment the recovery of thymopoiesis may improve outcomes after CBT.
Figures
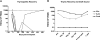


References
-
- Gluckman E, Broxmeyer HA, Auerbach AD, et al. Hematopoietic reconstitution in a patient with Fanconi's anemia by means of umbilical-cord blood from an HLA-identical sibling. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:1174–1178. - PubMed
-
- Kurtzberg J, Laughlin M, Graham ML, et al. Placental blood as a source of hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation into unrelated recipients. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:157–166. - PubMed
-
- Laughlin MJ, Barker J, Bambach B, et al. Hematopoietic engraftment and survival in adult recipients of umbilical-cord blood from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1815–1822. - PubMed
-
- Rubinstein P, Carrier C, Scaradavou A, et al. Outcomes among 562 recipients of placental-blood transplants from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1565–1577. - PubMed
-
- Gluckman E, Rocha V, Chevret S. Results of unrelated umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Rev Clin Exp Hematol. 2001;5:87–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

