Role of survivin phosphorylation by aurora B in mitosis
- PMID: 17671419
- PMCID: PMC3323923
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.6.15.4482
Role of survivin phosphorylation by aurora B in mitosis
Abstract
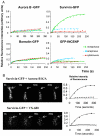
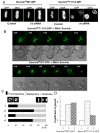
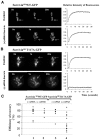
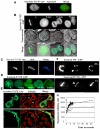
The chromosomal protein passenger complex, a key mitotic regulator, consists of at least four proteins, INCENP, Aurora B, Survivin and Borealin. Survivin, in contrast to the other members of the chromosomal protein passenger complex (CPC), is mobile at metaphase. This protein is also phosphorylated by Aurora B at Threonine 117. In this work we have studied the role of the phosphorylation of Survivin in mitosis by using non phosphorylable T117A and phosphomimic T117E silent resistant Survivin mutants, inducible cell lines expressing these mutants and a combination of siRNA, time-lapse microscopy and FRAP analysis. Time lapse microscopy and FRAP analysis show that Survivin T117A mutant is very stably associated with centromeres and its expression induces a prometaphasic arrest in endogenous survivin depleted cells. In addition, Survivin T117A was unable to rescue the phenotypes of the endogenous survivin depleted cells. Expressed in these cells, the phosphomimic Survivin T117E mutant exhibits a very weak interaction with the centromeres and behaves as a dominant negative mutant inducing severe mitotic defects. Our data suggest that the Aurora B generated phosphorylation/dephosphorylation cycle of Survivin is required for proper proceeding of mitosis.
Figures
References
-
- Adams RR, Carmena M, Earnshaw WC. Chromosomal passengers and the (aurora) ABCs of mitosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:49–54. - PubMed
-
- Andrews PD, Ovechkina Y, Morrice N, Wagenbach M, Duncan K, Wordeman L, Swedlow JR. Aurora B regulates MCAK at the mitotic centromere. Dev Cell. 2004;6:253–268. - PubMed
-
- Hirota T, Lipp JJ, Toh BH, Peters JM. Histone H3 serine 10 phosphorylation by Aurora B causes HP1 dissociation from heterochromatin. Nature. 2005;438:1176–1180. - PubMed
-
- Nowak SJ, Corces VG. Phosphorylation of histone H3: a balancing act between chromosome condensation and transcriptional activation. Trends Genet. 2004;20:214–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
