ErbB receptors: from oncogenes to targeted cancer therapies
- PMID: 17671639
- PMCID: PMC1934579
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI32278
ErbB receptors: from oncogenes to targeted cancer therapies
Abstract
Understanding the genetic origin of cancer at the molecular level has facilitated the development of novel targeted therapies. Aberrant activation of the ErbB family of receptors is implicated in many human cancers and is already the target of several anticancer therapeutics. The use of mAbs specific for the extracellular domain of ErbB receptors was the first implementation of rational targeted therapy. The cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain is also a preferred target for small compounds that inhibit the kinase activity of these receptors. However, current therapy has not yet been optimized, allowing for opportunities for optimization of the next generation of targeted therapy, particularly with regards to inhibiting heteromeric ErbB family receptor complexes.
Figures
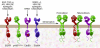
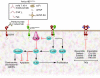
References
-
- Nowell P.C., Hungerford D.A. A minute chromosome in human chronic granulocytic leukemia. Science. 1960;132:1497. - PubMed
-
- Rowley J.D. Letter: A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature. 1973;243:290–293. - PubMed
-
- Druker B.J., et al. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat. Med. 1996;2:561–566. - PubMed
-
- Yarden Y., Sliwkowski M.X. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001;2:127–137. - PubMed
-
- Slamon D.J., et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;344:783–792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

