Proteolytic processing of dynamin by cytoplasmic cathepsin L is a mechanism for proteinuric kidney disease
- PMID: 17671649
- PMCID: PMC1934589
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI32022
Proteolytic processing of dynamin by cytoplasmic cathepsin L is a mechanism for proteinuric kidney disease
Abstract
Kidney podocytes and their foot processes maintain the ultrafiltration barrier and prevent urinary protein loss (proteinuria). Here we show that the GTPase dynamin is essential for podocyte function. During proteinuric kidney disease, induction of cytoplasmic cathepsin L leads to cleavage of dynamin at an evolutionary conserved site, resulting in reorganization of the podocyte actin cytoskeleton and proteinuria. Dynamin mutants that lack the cathepsin L site, or render the cathepsin L site inaccessible through dynamin self-assembly, are resistant to cathepsin L cleavage. When delivered into mice, these mutants restored podocyte function and resolve proteinuria. Our study identifies dynamin as a critical regulator of renal permselectivity that is specifically targeted by proteolysis under pathological conditions.
Figures
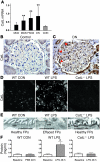

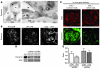
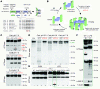


Comment in
-
Proteinuria: is it all in the foot?J Clin Invest. 2007 Aug;117(8):2079-82. doi: 10.1172/JCI32966. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17671644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zandi-Nejad K., Eddy A.A., Glassock R.J., Brenner B.M. Why is proteinuria an ominous biomarker of progressive kidney disease? . Kidney Int. Suppl. 2004;66:S76–S89. - PubMed
-
- Tryggvason K., Patrakka J., Wartiovaara J. Hereditary proteinuria syndromes and mechanisms of proteinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;354:1387–1401. - PubMed
-
- Reiser J., et al. Podocyte migration during nephrotic syndrome requires a coordinated interplay between cathepsin l and alpha3 integrin. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:34827–34832. - PubMed
-
- Baricos W.H., O’Connor S.E., Cortez S.L., Wu L.T., Shah S.V. The cysteine proteinase inhibitor, E-64, reduces proteinuria in an experimental model of glomerulonephritis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988;155:1318–1323. - PubMed
-
- Goulet B., et al. A cathepsin L isoform that is devoid of a signal peptide localizes to the nucleus in S phase and processes the CDP/Cux transcription factor. Mol. Cell. 2004;14:207–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

