Mechanisms by which common variants in the TCF7L2 gene increase risk of type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 17671651
- PMCID: PMC1934596
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI30706
Mechanisms by which common variants in the TCF7L2 gene increase risk of type 2 diabetes
Abstract
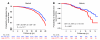
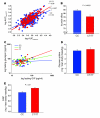
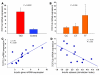
Genetic variants in the gene encoding for transcription factor-7-like 2 (TCF7L2) have been associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and impaired beta cell function, but the mechanisms have remained unknown. We therefore studied prospectively the ability of common variants in TCF7L2 to predict future T2D and explored the mechanisms by which they would do this. Scandinavian subjects followed for up to 22 years were genotyped for 3 SNPs (rs7903146, rs12255372, and rs10885406) in TCF7L2, and a subset of them underwent extensive metabolic studies. Expression of TCF7L2 was related to genotype and metabolic parameters in human islets. The CT/TT genotypes of SNP rs7903146 strongly predicted future T2D in 2 independent cohorts (Swedish and Finnish). The risk T allele was associated with impaired insulin secretion, incretin effects, and enhanced rate of hepatic glucose production. TCF7L2 expression in human islets was increased 5-fold in T2D, particularly in carriers of the TT genotype. Overexpression of TCF7L2 in human islets reduced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. In conclusion, the increased risk of T2D conferred by variants in TCF7L2 involves the enteroinsular axis, enhanced expression of the gene in islets, and impaired insulin secretion.
Figures


Comment in
-
Prime suspect: the TCF7L2 gene and type 2 diabetes risk.J Clin Invest. 2007 Aug;117(8):2077-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI33077. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17671643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gloyn A.L., et al. Large-scale association studies of variants in genes encoding the pancreatic beta-cell KATP channel subunits Kir6.2 (KCNJ11) and SUR1 (ABCC8) confirm that the KCNJ11 E23K variant is associated with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003;52:568–572. - PubMed
-
- Altshuler D., et al. The common PPARgamma Pro12Ala polymorphism is associated with decreased risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2000;26:76–80. - PubMed
-
- Florez J.C., et al. Haplotype structure and genotype-phenotype correlations of the sulfonylurea receptor and the islet ATP-sensitive potassium channel gene region. Diabetes. 2004;53:1360–1368. - PubMed
-
- Grant S.F., et al. Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:320–323. - PubMed
-
- Groves C.J., et al. Association analysis of 6,736 U.K. subjects provides replication and confirms TCF7L2 as a type 2 diabetes susceptibility gene with a substantial effect on individual risk. Diabetes. 2006;55:2640–2644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

