Gammaretrovirus-mediated correction of SCID-X1 is associated with skewed vector integration site distribution in vivo
- PMID: 17671654
- PMCID: PMC1934556
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI31661
Gammaretrovirus-mediated correction of SCID-X1 is associated with skewed vector integration site distribution in vivo
Abstract
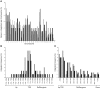
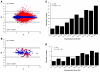
We treated 10 children with X-linked SCID (SCID-X1) using gammaretrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Those with sufficient follow-up were found to have recovered substantial immunity in the absence of any serious adverse events up to 5 years after treatment. To determine the influence of vector integration on lymphoid reconstitution, we compared retroviral integration sites (RISs) from peripheral blood CD3(+) T lymphocytes of 5 patients taken between 9 and 30 months after transplantation with transduced CD34(+) progenitor cells derived from 1 further patient and 1 healthy donor. Integration occurred preferentially in gene regions on either side of transcription start sites, was clustered, and correlated with the expression level in CD34(+) progenitors during transduction. In contrast to those in CD34(+) cells, RISs recovered from engrafted CD3(+) T cells were significantly overrepresented within or near genes encoding proteins with kinase or transferase activity or involved in phosphorus metabolism. Although gross patterns of gene expression were unchanged in transduced cells, the divergence of RIS target frequency between transduced progenitor cells and post-thymic T lymphocytes indicates that vector integration influences cell survival, engraftment, or proliferation.
Figures

Comment in
-
Retroviral integration and human gene therapy.J Clin Invest. 2007 Aug;117(8):2083-6. doi: 10.1172/JCI32949. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17671645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cavazzana-Calvo M., et al. Gene therapy of human severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)-X1 disease. Science. 2000;288:669–672. - PubMed
-
- Gaspar H.B., et al. Gene therapy of X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency by use of a pseudotyped gammaretroviral vector. Lancet. . 2004;364:2181–2187. - PubMed
-
- Hacein-Bey-Abina S., et al. Sustained correction of X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency by ex vivo gene therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;346:1185–1193. - PubMed
-
- Aiuti A., et al. Correction of ADA-SCID by stem cell gene therapy combined with nonmyeloablative conditioning. Science. 2002;296:2410–2413. - PubMed
-
- Aiuti A., et al. Immune reconstitution in ADA-SCID after PBL gene therapy and discontinuation of enzyme replacement. Nat. Med. 2002;8:423–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

