AMPK is essential for energy homeostasis regulation and glucose sensing by POMC and AgRP neurons
- PMID: 17671657
- PMCID: PMC1934578
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI31516
AMPK is essential for energy homeostasis regulation and glucose sensing by POMC and AgRP neurons
Abstract
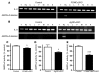
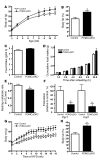
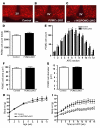
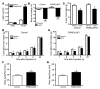
Hypothalamic AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) has been suggested to act as a key sensing mechanism, responding to hormones and nutrients in the regulation of energy homeostasis. However, the precise neuronal populations and cellular mechanisms involved are unclear. The effects of long-term manipulation of hypothalamic AMPK on energy balance are also unknown. To directly address such issues, we generated POMC alpha 2KO and AgRP alpha 2KO mice lacking AMPK alpha2 in proopiomelanocortin- (POMC-) and agouti-related protein-expressing (AgRP-expressing) neurons, key regulators of energy homeostasis. POMC alpha 2KO mice developed obesity due to reduced energy expenditure and dysregulated food intake but remained sensitive to leptin. In contrast, AgRP alpha 2KO mice developed an age-dependent lean phenotype with increased sensitivity to a melanocortin agonist. Electrophysiological studies in AMPK alpha2-deficient POMC or AgRP neurons revealed normal leptin or insulin action but absent responses to alterations in extracellular glucose levels, showing that glucose-sensing signaling mechanisms in these neurons are distinct from those pathways utilized by leptin or insulin. Taken together with the divergent phenotypes of POMC alpha 2KO and AgRP alpha 2KO mice, our findings suggest that while AMPK plays a key role in hypothalamic function, it does not act as a general sensor and integrator of energy homeostasis in the mediobasal hypothalamus.
Figures
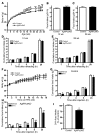

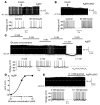
Comment in
-
"AMPing up" our understanding of the hypothalamic control of energy balance.J Clin Invest. 2007 Aug;117(8):2089-92. doi: 10.1172/JCI32975. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17671647 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
"AMPing up" our understanding of the hypothalamic control of energy balance.J Clin Invest. 2007 Aug;117(8):2089-92. doi: 10.1172/JCI32975. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17671647 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Lkb1 in pro-opiomelanocortin neurons impairs peripheral glucose homeostasis in mice.Diabetes. 2011 Mar;60(3):735-45. doi: 10.2337/db10-1055. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21266325 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal S6K1 in POMC and AgRP Neurons Regulates Glucose Homeostasis but Not Feeding Behavior in Mice.Cell Rep. 2015 Apr 21;11(3):335-43. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.03.029. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25865886 Free PMC article.
-
Hormone and glucose signalling in POMC and AgRP neurons.J Physiol. 2009 Nov 15;587(Pt 22):5305-14. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.179192. Epub 2009 Sep 21. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19770186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrophysiological Mechanism of Peripheral Hormones and Nutrients Regulating Energy Homeostasis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1090:183-198. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-1286-1_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30390291 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Insights into the Role of Hypothalamic AMPK Signaling Cascade upon Metabolic Control.Front Neurosci. 2012 Dec 20;6:185. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00185. eCollection 2012. Front Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23267314 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 upregulation in hypothalamic leptin resistance and long-term energy homeostasis.Diabetes. 2010 Apr;59(4):894-906. doi: 10.2337/db09-1024. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 20068134 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose regulates hypothalamic long-chain fatty acid metabolism via AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) in neurons and astrocytes.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 27;288(52):37216-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.506238. Epub 2013 Nov 15. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24240094 Free PMC article.
-
CRH-R2 signalling modulates feeding and circadian gene expression in hypothalamic mHypoA-2/30 neurons.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 11;14:1266081. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1266081. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37900150 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of glucose sensing and leptin action in the brain.Mol Metab. 2020 Sep;39:101011. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101011. Epub 2020 May 13. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32416314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kahn B.B., Alquier T., Carling D., Hardie D.G. AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 2005;1:15–25. - PubMed
-
- Hawley S.A., et al. Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-beta is an alternative upstream kinase for AMP-activated protein kinase. Cell Metab. 2005;2:9–19. - PubMed
-
- Woods A., et al. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-beta acts upstream of AMP-activated protein kinase in mammalian cells. Cell Metab. 2005;2:21–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

