Gambogic acid, a novel ligand for transferrin receptor, potentiates TNF-induced apoptosis through modulation of the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway
- PMID: 17673602
- PMCID: PMC2077305
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-03-079616
Gambogic acid, a novel ligand for transferrin receptor, potentiates TNF-induced apoptosis through modulation of the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway
Expression of concern in
-
Pandey MK, Sung B, Ahn KS, Kunnumakkara AB, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB. Gambogic acid, a novel ligand for transferrin receptor, potentiates TNF-induced apoptosis through modulation of the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. Blood. 2007;110(10):3517-3525.Blood. 2013 May 2;121(18):3778. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-03-494385. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23640997 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
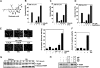
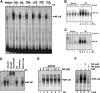
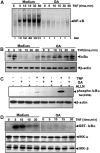
Gambogic acid (GA), a xanthone derived from the resin of the Garcinia hanburyi, has been recently demonstrated to bind transferrin receptor and exhibit potential anticancer effects through a signaling mechanism that is not fully understood. Because of the critical role of NF-kappaB signaling pathway, we investigated the effects of GA on NF-kappaB-mediated cellular responses and NF-kappaB-regulated gene products in human leukemia cancer cells. Treatment of cells with GA enhanced apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and chemotherapeutic agents, inhibited the expression of gene products involved in antiapoptosis (IAP1 and IAP2, Bcl-2, Bcl-x(L), and TRAF1), proliferation (cyclin D1 and c-Myc), invasion (COX-2 and MMP-9), and angiogenesis (VEGF), all of which are known to be regulated by NF-kappaB. GA suppressed NF-kappaB activation induced by various inflammatory agents and carcinogens and this, accompanied by the inhibition of TAK1/TAB1-mediated IKK activation, inhibited IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and degradation, suppressed p65 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation, and finally abrogated NF-kappaB-dependent reporter gene expression. The NF-kappaB activation induced by TNFR1, TRADD, TRAF2, NIK, TAK1/TAB1, and IKKbeta was also inhibited. The effect of GA mediated through transferrin receptor as down-regulation of the receptor by RNA interference reversed its effects on NF-kappaB and apoptosis. Overall our results demonstrate that GA inhibits NF-kappaB signaling pathway and potentiates apoptosis through its interaction with the transferrin receptor.
Figures




References
-
- Aggarwal BB, Ichikawa H, Garodia P, et al. From traditional Ayurvedic medicine to modern medicine: identification of therapeutic targets for suppression of inflammation and cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2006;10:87–118. - PubMed
-
- Newman DJ, Cragg GM, Snader KM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J Nat Prod. 2003;66:1022–1037. - PubMed
-
- Guo QL, Lin SS, You QD, et al. Inhibition of human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene expression by gambogic acid in human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells. Life Sci. 2006;78:1238–1245. - PubMed
-
- Zhang HZ, Kasibhatla S, Wang Y, et al. Discovery, characterization and SAR of gambogic acid as a potent apoptosis inducer by a HTS assay. Bioorg Med Chem. 2004;12:309–317. - PubMed
-
- Zhao L, Guo QL, You QD, Wu ZQ, Gu HY. Gambogic acid induces apoptosis and regulates expressions of Bax and Bcl-2 protein in human gastric carcinoma MGC-803 cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004;27:998–1003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

