Cerebral ischemia detected with diffusion-weighted MR imaging after protected carotid artery stenting: comparison of distal balloon and filter device
- PMID: 17673838
- PMCID: PMC2627162
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2007.8.4.276
Cerebral ischemia detected with diffusion-weighted MR imaging after protected carotid artery stenting: comparison of distal balloon and filter device
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to examine the incidence of ischemia during protected carotid artery stenting (CAS) as well as to compare the protective efficacy of the balloon and filter devices on diffusion-weighted MR imaging (DWI).
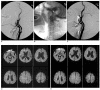
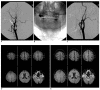
Materials and methods: Seventy-one consecutive protected CAS procedures in 70 patients with a severe (> 70%) or symptomatic moderate (> 50%) carotid artery stenosis were examined. A balloon device (PercuSurge GuardWire) and a filter device (FilterWire EX/EZ, Emboshield) was used in 33 cases (CAS-B group) and 38 cases (CAS-F group) to prevent distal embolization, respectively. All the patients underwent DWI within seven days before and after the procedures. The number of new cerebral ischemic lesions on the post-procedural DWI were counted and divided into ipsilateral and contralateral lesions according to the relationship with the stenting side.
Results: New cerebral ischemic lesions were detected in 13 (39.4%) out of the 33 CAS-Bs and in 15 (39.5%) out of the 38 CAS-Fs. The mean number of total, ipsilateral and contralateral new cerebral ischemic lesion was 2.39, 1.67 and 0.73 in the CAS-B group and 2.11, 1.32 and 0.79 in the CAS-F group, respectively. No statistical differences were found between the two groups (p = 0.96, 0.74 and 0.65, respectively). The embolic complications encountered included two retinal infarctions and one hemiparesis in the CAS-B group (9.09%), and one retinal infarction, one hemiparesis and one ataxia in the CAS-F group (7.89%). There was a similar incidence of embolic complications in the two groups (p = 1.00).
Conclusion: The type of distal protection device used such as a balloon and filter does not affect the incidence of cerebral embolization after protected CAS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cerebral ischemic lesions detected with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging after carotid artery stenting: Comparison of several anti-embolic protection devices.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2009 Sep;49(9):386-93. doi: 10.2176/nmc.49.386. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2009. PMID: 19779282
-
The PROFI study (Prevention of Cerebral Embolization by Proximal Balloon Occlusion Compared to Filter Protection During Carotid Artery Stenting): a prospective randomized trial.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Apr 10;59(15):1383-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.11.035. Epub 2012 Jan 25. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22284330 Clinical Trial.
-
Embolism to the brain during carotid stenting and surgery.Acta Chir Belg. 2007 Mar-Apr;107(2):151-4. Acta Chir Belg. 2007. PMID: 17515263
-
Cerebral embolic lesions detected with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging following carotid artery stenting: a meta-analysis of 8 studies comparing filter cerebral protection and proximal balloon occlusion.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014 Oct;7(10):1177-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2014.05.019. Epub 2014 Sep 17. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014. PMID: 25240544 Review.
-
Evidence overview: benefit of cerebral protection devices during carotid artery stenting.J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2017 Apr;58(2):170-177. doi: 10.23736/S0021-9509.16.09848-7. Epub 2016 Dec 22. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2017. PMID: 28004899 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety and Efficacy of Flow Reversal in Acute and Elective Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting Using the Mo.Ma Device with Short-Term Follow-Up.Interv Neurol. 2020 Jan;8(2-6):196-205. doi: 10.1159/000499045. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Interv Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32508902 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance plaque imaging to predict the occurrence of the slow-flow phenomenon in carotid artery stenting procedures.Neuroradiology. 2010 Apr;52(4):275-83. doi: 10.1007/s00234-009-0623-7. Neuroradiology. 2010. PMID: 19936732
-
Ophthalmic artery occlusion after carotid revascularization.J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2013 Dec;15(4):326-9. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2013.15.4.326. Epub 2013 Dec 31. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2013. PMID: 24729961 Free PMC article.
-
Use of embolic protective devices in treating acute arterial occlusions: an interventional radiology and vascular surgery collaborative learning experience.BMJ Case Rep. 2013 Apr 10;2013:bcr2012008132. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2012-008132. BMJ Case Rep. 2013. PMID: 23580669 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment outcomes of carotid artery stenting with two types of distal protection filter device.Springerplus. 2014 Mar 8;3:132. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-3-132. eCollection 2014. Springerplus. 2014. PMID: 25674435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beauchamp NJ, Jr, Barker PB, Wang PY, vanZijl PC. Imaging of acute cerebral ischemia. Radiology. 1999;212:307–324. - PubMed
-
- van Everdingen KJ, van der Grond J, Kappelle LJ, Ramos LM, Mali WP. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in acute stroke. Stroke. 1998;29:1783–1790. - PubMed
-
- Barth A, Remonda L, Lövblad KO, Schroth G, Seiler RW. Silent cerebral ischemia detected by diffusion-weighted MRI after carotid endarterectomy. Stroke. 2000;31:1824–1828. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

