Chronic olanzapine activates the Stat3 signal transduction pathway and alters expression of components of the 5-HT2A receptor signaling system in rat frontal cortex
- PMID: 17675105
- PMCID: PMC2075101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.06.019
Chronic olanzapine activates the Stat3 signal transduction pathway and alters expression of components of the 5-HT2A receptor signaling system in rat frontal cortex
Abstract
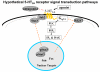
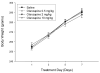
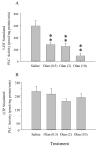
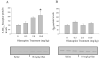
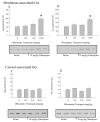
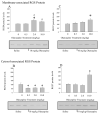
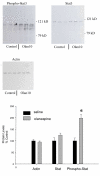
The mechanisms underlying desensitization of serotonin 2A (5-HT(2A)) receptor signaling by antagonists are unclear but may involve changes in gene expression mediated via signal transduction pathways. In cells in culture, olanzapine causes desensitization of 5-HT(2A) receptor signaling and increases the levels of regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) 7 protein dependent on phosphorylation/activation of the Janus kinase 2 (Jak2)/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (Stat3) signaling pathway. In the current study, the 5-HT(2A) receptor signaling system in rat frontal cortex was examined following 7 days of daily treatment with 0.5, 2.0 or 10.0 mg/kg i.p. olanzapine. Olanzapine increased phosphorylation of Stat3 in rats treated daily with 10 mg/kg olanzapine and caused a dose-dependent desensitization of 5-HT(2A) receptor-mediated phospholipase C activity. There were dose-dependent increases in the levels of membrane-associated 5-HT(2A) receptor, G(alpha11) and G(alphaq) protein levels but no changes in the G(beta) protein levels. With olanzapine treatment, RGS4 protein levels increase in the membrane-fraction and decrease in the cytosolic fraction by similar amounts suggesting a redistribution of RGS4 protein within neurons. RGS7 protein levels increase in both the membrane and cytosolic fractions in rats treated daily with 10mg/kg olanzapine. The olanzapine-induced increase in Stat3 activity could underlie the increase in RGS7 protein expression in vivo as previously demonstrated in cultured cells. Furthermore, the increases in membrane-associated RGS proteins could play a role in desensitization of signaling by terminating the activated G(alphaq/11) proteins more rapidly.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of the JAK-STAT pathway by olanzapine is necessary for desensitization of serotonin2A receptor-stimulated phospholipase C signaling in rat frontal cortex but not serotonin2A receptor-stimulated hormone release.J Psychopharmacol. 2010 Jul;24(7):1079-88. doi: 10.1177/0269881109103090. Epub 2009 Mar 20. J Psychopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19304867 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the JAK-STAT pathway is necessary for desensitization of 5-HT2A receptor-stimulated phospholipase C signalling by olanzapine, clozapine and MDL 100907.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009 Jun;12(5):651-65. doi: 10.1017/S1461145708009590. Epub 2008 Oct 31. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18976543 Free PMC article.
-
Olanzapine increases RGS7 protein expression via stimulation of the Janus tyrosine kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling cascade.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Jul;322(1):133-40. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.120386. Epub 2007 Mar 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17392403
-
Agonist-induced serotonin 2A receptor desensitization in the rat frontal cortex and hypothalamus.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Jun;309(3):1043-50. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.062067. Epub 2004 Feb 19. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004. PMID: 14976228
-
Agonist induced-phosphorylation of Galpha11 protein reduces coupling to 5-HT2A receptors.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Oct;323(1):248-56. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.122317. Epub 2007 Jul 23. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17646429
Cited by
-
Evaluating the potential for rostral diffusion in the cerebral ventricles using angiotensin II-induced drinking in rats.Brain Res. 2012 Nov 27;1486:62-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.09.040. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 23026079 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and cancer: how intimate is the relationship?Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Aug;1171:59-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04911.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19723038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain RGS4 and RGS10 protein expression in schizophrenia and depression. Effect of drug treatment.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Mar;226(1):177-88. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2888-5. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23093381
-
Lower phosphorylated glycogen synthase kinase-3B levels in platelets of patients with schizophrenia: increment by olanzapine treatment.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2015 Mar;265(2):167-70. doi: 10.1007/s00406-014-0505-9. Epub 2014 May 15. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 24831601
-
Increased hypothalamic signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 phosphorylation after hindbrain leptin injection.Endocrinology. 2010 Apr;151(4):1509-19. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0854. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20185769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anji A, Kumari M, Hanley NRS, Bryan GL, Hensler JG. Regulation of 5-HT2A receptor mRNA levels and binding sites in rat frontal cortex by the agonist DOI and the antagonist mianserin. Neuropharmacology. 2000;39:1996–2005. - PubMed
-
- Aravagiri M, Teper Y, Marder SR. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of olanzapine in rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1999;20:369–377. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia G, Cabrera-Vera TM, Van de Kar LD. Prenatal cocaine exposure potentiates 5-HT2A receptor function in male and female rat offspring. Synapse. 2000;35:163–172. - PubMed
-
- Bhatnagar A, Willins DL, Gray JA, Woods J, Benovic JL, Roth BL. The dynamin-dependent, arrestin-independent internalization of 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A (5-HT2A) serotonin receptors reveals differential sorting of arrestins and 5-HT2A receptors during endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:8269–8277. - PubMed
-
- Burchett SA. In through the out door: nuclear localization of the regulators of G protein signaling. J Neurochem. 2003;87:551–559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

