Chronic olanzapine activates the Stat3 signal transduction pathway and alters expression of components of the 5-HT2A receptor signaling system in rat frontal cortex
- PMID: 17675105
- PMCID: PMC2075101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.06.019
Chronic olanzapine activates the Stat3 signal transduction pathway and alters expression of components of the 5-HT2A receptor signaling system in rat frontal cortex
Abstract
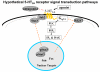
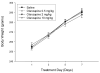
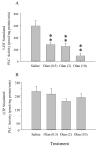
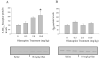
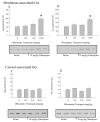
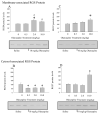
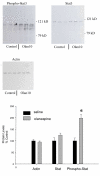
The mechanisms underlying desensitization of serotonin 2A (5-HT(2A)) receptor signaling by antagonists are unclear but may involve changes in gene expression mediated via signal transduction pathways. In cells in culture, olanzapine causes desensitization of 5-HT(2A) receptor signaling and increases the levels of regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) 7 protein dependent on phosphorylation/activation of the Janus kinase 2 (Jak2)/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (Stat3) signaling pathway. In the current study, the 5-HT(2A) receptor signaling system in rat frontal cortex was examined following 7 days of daily treatment with 0.5, 2.0 or 10.0 mg/kg i.p. olanzapine. Olanzapine increased phosphorylation of Stat3 in rats treated daily with 10 mg/kg olanzapine and caused a dose-dependent desensitization of 5-HT(2A) receptor-mediated phospholipase C activity. There were dose-dependent increases in the levels of membrane-associated 5-HT(2A) receptor, G(alpha11) and G(alphaq) protein levels but no changes in the G(beta) protein levels. With olanzapine treatment, RGS4 protein levels increase in the membrane-fraction and decrease in the cytosolic fraction by similar amounts suggesting a redistribution of RGS4 protein within neurons. RGS7 protein levels increase in both the membrane and cytosolic fractions in rats treated daily with 10mg/kg olanzapine. The olanzapine-induced increase in Stat3 activity could underlie the increase in RGS7 protein expression in vivo as previously demonstrated in cultured cells. Furthermore, the increases in membrane-associated RGS proteins could play a role in desensitization of signaling by terminating the activated G(alphaq/11) proteins more rapidly.
Figures
References
-
- Anji A, Kumari M, Hanley NRS, Bryan GL, Hensler JG. Regulation of 5-HT2A receptor mRNA levels and binding sites in rat frontal cortex by the agonist DOI and the antagonist mianserin. Neuropharmacology. 2000;39:1996–2005. - PubMed
-
- Aravagiri M, Teper Y, Marder SR. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of olanzapine in rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1999;20:369–377. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia G, Cabrera-Vera TM, Van de Kar LD. Prenatal cocaine exposure potentiates 5-HT2A receptor function in male and female rat offspring. Synapse. 2000;35:163–172. - PubMed
-
- Bhatnagar A, Willins DL, Gray JA, Woods J, Benovic JL, Roth BL. The dynamin-dependent, arrestin-independent internalization of 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A (5-HT2A) serotonin receptors reveals differential sorting of arrestins and 5-HT2A receptors during endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:8269–8277. - PubMed
-
- Burchett SA. In through the out door: nuclear localization of the regulators of G protein signaling. J Neurochem. 2003;87:551–559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

