Brevetoxins, like ciguatoxins, are potent ichthyotoxic neurotoxins that accumulate in fish
- PMID: 17675204
- PMCID: PMC2652748
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2007.06.005
Brevetoxins, like ciguatoxins, are potent ichthyotoxic neurotoxins that accumulate in fish
Abstract
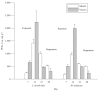
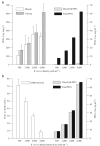
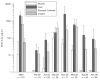
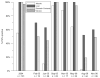
Brevetoxins and ciguatoxins are closely related potent marine neurotoxins. Although ciguatoxins accumulate in fish to levels that are dangerous for human consumption, live fish have not been considered as potential sources of brevetoxin exposure in humans. Here we show that, analogous to ciguatoxins, brevetoxins can accumulate in live fish by dietary transfer. We experimentally identify two pathways leading to brevetoxin-contaminated omnivorous and planktivorous fish. Fish fed with toxic shellfish and Karenia brevis cultures remained healthy and accumulated high brevetoxin levels in their tissues (up to 2675 ng g(-1) in viscera and 1540 ng g(-1) in muscle). Repeated collections of fish from St. Joseph Bay in the Florida panhandle reveal that accumulation of brevetoxins in healthy fish occurs in the wild. We observed that levels of brevetoxins in the muscle of fish at all trophic levels rise significantly, but not to dangerous levels, during a K. brevis bloom. Concentrations were highest in fish liver and stomach contents, and increased during and immediately following the bloom. The persistence of brevetoxins in the fish food web was followed for 1 year after the K. brevis bloom.
Figures


References
-
- Abbott BC, Siger A, Spigelstein M. Toxins from the blooms of Gymnodinium breve. In: LoCicero VR, editor. Proceedings of the First International Conference on Toxic Dinoflagellate Blooms; Wakefield: Massachusetts Science and Technology Foundation; 1975. pp. 355–366.
-
- Adachi R, Fukuyo Y. The thecal structure of a marine toxic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus gen. et sp. nov. collected in a ciguatera-endemic area. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish. 1979;45:67–71.
-
- Anderson DM, Lobel PS. The continuing enigma of ciguatera. Biol Bull. 1987;172:89–107.
-
- APHA. Recommended Procedures for the Examination of Sea Water and Shellfish. fourth. American Public Health Association; Washington, DC: 1970. Subcommittee on laboratory methods for the examination of shellfish Method for the bioassay of Gymnodinium breve toxin(s) in shellfish; pp. 61–66.
-
- Baden DG. Public health problems of red tides. In: Tu AT, editor. Handbook of Natural Toxins, vol 3: Marine Toxins and Venoms. Marcel Dekker, Inc.; New York: 1988. pp. 259–277.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

