Control of methionine synthesis and uptake by MetR and homocysteine in Streptococcus mutans
- PMID: 17675375
- PMCID: PMC2045202
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00703-07
Control of methionine synthesis and uptake by MetR and homocysteine in Streptococcus mutans
Abstract
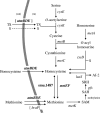
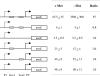
MetR (formerly Smu.1225), a regulator of the LysR family, controls key genes for methionine supply in Streptococcus mutans. An S. mutans metR mutant is unable to transport l-methionine and to grow in the absence of this amino acid. Accordingly, MetR activates transcription by binding to the promoter regions of two gene clusters and smu.1487, whose products are involved in methionine biosynthesis (MetEF and Smu.1487) and uptake (AtmBDE). Transcriptional activation by MetR requires the presence of a 17-bp palindromic sequence, the Met box. Base substitutions in the Met box hinder the formation of a MetR-DNA complex and abolish MetR-dependent activation, showing that Met boxes correspond to MetR recognition sites. Activation by MetR occurs in methionine-depleted medium and is rapidly triggered under nonactivating conditions by the addition of homocysteine. This intermediate of methionine biosynthesis increases the affinity of MetR for DNA in vitro and appears to be the MetR coeffector in vivo. Homocysteine plays a crucial role in methionine metabolic gene regulation by controlling MetR activity. A similar mechanism of homocysteine- and MetR-dependent control of methionine biosynthetic genes operates in S. thermophilus. These data suggest a common mechanism for the regulation of the methionine supply in streptococci. However, some streptococcal species are unable to synthesize the homocysteine coeffector. This intriguing feature is discussed in the light of comparative genomics and streptococcal ecology.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Three paralogous LysR-type transcriptional regulators control sulfur amino acid supply in Streptococcus mutans.J Bacteriol. 2010 Jul;192(13):3464-73. doi: 10.1128/JB.00119-10. Epub 2010 Apr 23. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20418399 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the methionine and cysteine transport and metabolism in streptococci.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 Nov;276(2):207-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00934.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17956428
-
Activation of the SMU.1882 transcription by CovR in Streptococcus mutans.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 22;5(11):e15528. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015528. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21124877 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of methionine synthesis in Escherichia coli.Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1593-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01905.x. Mol Microbiol. 1991. PMID: 1943695 Review.
-
Independent evolution of competence regulatory cascades in streptococci?Trends Microbiol. 2006 Aug;14(8):339-45. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2006.06.007. Epub 2006 Jul 3. Trends Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16820295 Review.
Cited by
-
The scfCDE Operon Encodes a Predicted ABC Importer Required for Fitness and Virulence during Group A Streptococcus Invasive Infection.Infect Immun. 2019 Nov 18;87(12):e00613-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00613-19. Print 2019 Dec. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31591169 Free PMC article.
-
Global regulation of gene expression in response to cysteine availability in Clostridium perfringens.BMC Microbiol. 2010 Sep 7;10:234. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-234. BMC Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20822510 Free PMC article.
-
LysR-type transcriptional regulator FinR is required for phenazine and pyrrolnitrin biosynthesis in biocontrol Pseudomonas chlororaphis strain G05.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Oct;105(20):7825-7839. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11600-8. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34562115
-
Streptococcus adherence and colonization.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009 Sep;73(3):407-50, Table of Contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00014-09. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19721085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three paralogous LysR-type transcriptional regulators control sulfur amino acid supply in Streptococcus mutans.J Bacteriol. 2010 Jul;192(13):3464-73. doi: 10.1128/JB.00119-10. Epub 2010 Apr 23. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20418399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brush, A., and H. Paulus. 1971. The enzymic formation of O-acetylhomoserine in Bacillus subtilis and its regulation by methionine and S-adenosylmethionine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 45:735-741. - PubMed
-
- Chopin, A. 1993. Organization and regulation of genes for amino acid biosynthesis in lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 12:21-37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

